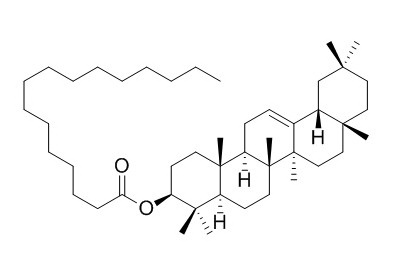
beta-Amyrin palmitate
Beta-Amyrin palmitate may release norepinephrine from newly synthesized pools, and thus, it may activate noradrenergic activity. Beta-Amyrin palmitate, like mianserin and imipramine, reduces the duration of immobility of mice significantly in a dose-dependent manner (5, 10 and 20 mg kg-1); (1)Beta-Amyrin palmitate or mianserin elicits a dose-related reduction in locomotor activity of mice and antagonizes locomotor stimulation induced by methamphetamine, imipramine increases locomotor activity and potentiates methamphetamine-induced hyperactivity; (2)Beta-Amyrin palmitate shows no effect on reserpine-induced hypothermia, whilst mianserin (10 mg kg-1) and imipramine (10 and 20 mg kg-1) antagonizes the reserpine-induced effect; (3)Beta-amyrin palmitate has similar properties in some respects to mianserin and might possess a sedative action.
Inquire / Order:
manager@chemfaces.com
Technical Inquiries:
service@chemfaces.com
Tel:
+86-27-84237783
Fax:
+86-27-84254680
Address:
1 Building, No. 83, CheCheng Rd., Wuhan Economic and Technological Development Zone, Wuhan, Hubei 430056, PRC
Providing storage is as stated on the product vial and the vial is kept tightly sealed, the product can be stored for up to
24 months(2-8C).
Wherever possible, you should prepare and use solutions on the same day. However, if you need to make up stock solutions in advance, we recommend that you store the solution as aliquots in tightly sealed vials at -20C. Generally, these will be useable for up to two weeks. Before use, and prior to opening the vial we recommend that you allow your product to equilibrate to room temperature for at least 1 hour.
Need more advice on solubility, usage and handling? Please email to: service@chemfaces.com
The packaging of the product may have turned upside down during transportation, resulting in the natural compounds adhering to the neck or cap of the vial. take the vial out of its packaging and gently shake to let the compounds fall to the bottom of the vial. for liquid products, centrifuge at 200-500 RPM to gather the liquid at the bottom of the vial. try to avoid loss or contamination during handling.
Molecules.2022, 27(2):451.
Molecules.2021, 26(8):2161.
Enzyme Microb Technol.2022, 153:109941.
Environ Toxicol.2019, 34(4):513-520.
J Sep Sci.2022, 45(18):3556-3566.
Molecules.2022, 27(19):6681.
Inflammation.2015, 38(4):1502-16
BMC Complement Altern Med.2018, 18(1):221
Food Sci Biotechnol.2016, 25(5):1437-1442
Foods.2023, 12(6):1227.
Related and Featured Products
J Pharm Pharmacol. 1993 Jun;45(6):545-50.
Pharmacological properties of beta-amyrin palmitate, a novel centrally acting compound, isolated from Lobelia inflata leaves.[Pubmed:
8103103]
Effects of beta-Amyrin palmitate isolated from the leaves of Lobelia inflata were studied on the central nervous system of mice and were compared with those of antidepressant drugs, mianserin and imipramine.
METHODS AND RESULTS:
In the forced swimming test, beta-Amyrin palmitate, like mianserin and imipramine, reduced the duration of immobility of mice significantly in a dose-dependent manner (5, 10 and 20 mg kg-1). beta-Amyrin palmitate (5, 10 and 20 mg kg-1) or mianserin (5, 10 and 20 mg kg-1) elicited a dose-related reduction in locomotor activity of mice and antagonized locomotor stimulation induced by methamphetamine. In contrast, imipramine (5, 10 and 20 mg kg-1) increased locomotor activity and potentiated methamphetamine-induced hyperactivity. beta-Amyrin palmitate showed no effect on reserpine-induced hypothermia, whilst mianserin (10 mg kg-1) and imipramine (10 and 20 mg kg-1) antagonized the reserpine-induced effect. Unlike imipramine, beta-Amyrin palmitate and mianserin did not affect haloperidol-induced catalepsy, tetrabenazine-induced ptosis and apomorphine-induced stereotypy. beta-Amyrin palmitate and imipramine had no effects on the head-twitch response induced by 5-hydroxytryptophan, whereas mianserin (5, 10 and 20 mg kg-1) decreased it in a dose-dependent manner. A potentiating effect of beta-Amyrin palmitate (5, 10 and 20 mg kg-1) on narcosis induced by sodium pentobarbitone was stronger than that of imipramine (10, 20 and 40 mg kg-1) but weaker than that of mianserin (2.5, 5 and 10 mg kg-1).
CONCLUSIONS:
These results suggest that beta-Amyrin palmitate has similar properties in some respects to mianserin and might possess a sedative action.
J Pharm Pharmacol. 1993 Nov;45(11):1006-8.
An alpha-adrenoceptor-mediated mechanism of hypoactivity induced by beta-amyrin palmitate.[Pubmed:
7908030]
METHODS AND RESULTS:
Inhibitory effects of beta-Amyrin palmitate in locomotor activity of mice were studied by combining this compound with alpha-adrenergic agonists or antagonists and a dopaminergic agonist. beta-Amyrin palmitate (2.5, 5.0 and 10.0 mg kg-1, i.p.) decreased locomotor activity of mice in a dose-dependent manner. It enhanced hypoactivity of mice treated with clonidine (0.025 mg kg-1, i.p.) and antagonized hyperactivity produced by phenylephrine (40 micrograms, i.c.v.). The inhibitory action of beta-Amyrin palmitate was not affected by yohimbine (1.5 mg kg-1, i.p.), but was potentiated by prazosin (0.75 mg kg-1, i.p.). When combined with a dopaminergic agonist, apomorphine (2.0 mg kg-1, i.p.), beta-Amyrin palmitate (5.0 and 10.0 mg kg-1, i.p.) did not affect locomotor stimulation produced by apomorphine.
CONCLUSIONS:
These results suggest that beta-Amyrin palmitate might inhibit alpha 1-adrenoceptors.
Phytomedicine. 2012 Jun 15;19(8-9):682-5.
β-Amyrin acetate and β-amyrin palmitate as antidyslipidemic agents from Wrightia tomentosa leaves.[Pubmed:
22541636 ]
The ethanolic extract and fractions of Wrightia tomentosa Roem. & Schult (Apocynaceae) leaves were tested in vivo for their antidyslipidemic activity in high fat diet (HFD) induced dyslipidemic hamsters.
METHODS AND RESULTS:
Activity guided isolation resulted in identification of antidyslipidemic compounds β-Amyrin acetate and beta-Amyrin palmitate. β-Amyrin acetate and beta-Amyrin palmitate decrease the levels of LDL by 36% and 44%, and increase the HDL-C/TC ratio by 49% and 28%, respectively, at a dose of 10mg/kg. In addition, the isolated compounds β-Amyrin acetate and beta-Amyrin palmitate showed significant HMG-CoA-reductase inhibition, which was further established by docking studies.
Life Sci. 1993;52(3):289-96.
A possible mechanism of antidepressant activity of beta-amyrin palmitate isolated from Lobelia inflata leaves in the forced swimming test.[Pubmed:
8423710]
METHODS AND RESULTS:
A mechanism of antidepressant activity of beta-Amyrin palmitate was studied using the forced swimming method in mice. beta-Amyrin palmitate (10 mg/kg) reduced the increase in the duration of immobility induced by tetrabenazine (100 and 200 mg/kg), but showed no effect on that in mice treated with alpha-methyl-para-tyrosine (500 mg/kg). beta-Amyrin palmitate (5 and 10 mg/kg) decreased the duration of immobility in mice treated with desipramine plus 6-hydroxy-dopamine (50 micrograms/mouse), but did not affect that induced by nomifensine plus 6-hydroxydopamine. The decreased immobility produced by desipramine (15 mg/kg) was not affected by beta-Amyrin palmitate. A study of norepinephrine release in mouse brain synaptosomes indicated that beta-Amyrin palmitate caused a release of [3H]norepinephrine.
CONCLUSIONS:
The results of the present study suggest that beta-Amyrin palmitate might release norepinephrine from newly synthesized pools, and thus, it might activate noradrenergic activity.
Eur J Pharmacol. 2014 Jul 5;734:77-82.
Promising anti-diabetes mellitus activity in rats of β-amyrin palmitate isolated from Hemidesmus indicus roots.[Pubmed:
24726843 ]
While evaluating the toxicity of the tuberous root extracts of Hemidesmus indicus, a traditional medicinal plant, the glucose lowering property of the root was observed by the investigators. Therefore, it was thought of interest to isolate the anti-hyperglycemic principle from the root and determine its utility to develop an anti-diabetes mellitus medicine.
METHODS AND RESULTS:
The active principle was isolated from H. indicus root extract by anti-hyperglycemic activity guided chromatographic techniques. Glucose tolerance test in rats was used to evaluate the anti-hyperglycenic property. Anti-diabetes mellitus property was evaluated in alloxan-induced diabetic rats as well as streptozotocin-induced (type-2 model) diabetic rats. The active principle was isolated and identified with spectral data as beta-Amyrin palmitate. Although it is a known compound, its presence in H. indicus is not known previously. It was observed for the first time that beta-Amyrin palmitate has remarkable anti-hyperglycemic activity in orally glucose loaded rats. Further, interestingly, it exhibited excellent anti-diabetes mellitus activity in both alloxan-diabetic and streptozotocin-diabetic rats at a very low concentration (50μg/kg body weight).
CONCLUSIONS:
One of the mechanisms of action of beta-Amyrin palmitate appears to be blocking the entry of glucose from the intestine. beta-Amyrin palmitate is very promising to develop a medicine for diabetes for combination therapy and/or mono-therapy.