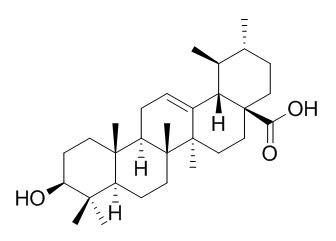
Ursolic acid
Ursolic acid is a potential PPARγagonist, which has anti-tumor, chemopreventive, hepatoprotective, anti-inflammatory, antioxidant, antidepressant-like, antimicrobial activities, and anti-asthmatic effects. Ursolic acid also has antihyperlipidemic, hypoglycemic and direct cardiac effect, its antihypertensive effect is attributed to its potent diuretic-natriuretic-saluretic activity. Ursolic acid regulates NF-κB, VEGF, COX-2, Nrf2, ARE, IL-5, IL-13, IL-17and MAPK signaling pathways.
Inquire / Order:
manager@chemfaces.com
Technical Inquiries:
service@chemfaces.com
Tel:
+86-27-84237783
Fax:
+86-27-84254680
Address:
1 Building, No. 83, CheCheng Rd., Wuhan Economic and Technological Development Zone, Wuhan, Hubei 430056, PRC
Providing storage is as stated on the product vial and the vial is kept tightly sealed, the product can be stored for up to
24 months(2-8C).
Wherever possible, you should prepare and use solutions on the same day. However, if you need to make up stock solutions in advance, we recommend that you store the solution as aliquots in tightly sealed vials at -20C. Generally, these will be useable for up to two weeks. Before use, and prior to opening the vial we recommend that you allow your product to equilibrate to room temperature for at least 1 hour.
Need more advice on solubility, usage and handling? Please email to: service@chemfaces.com
The packaging of the product may have turned upside down during transportation, resulting in the natural compounds adhering to the neck or cap of the vial. take the vial out of its packaging and gently shake to let the compounds fall to the bottom of the vial. for liquid products, centrifuge at 200-500 RPM to gather the liquid at the bottom of the vial. try to avoid loss or contamination during handling.
J Biochem Mol Toxicol.2020, 34(7):e22489.
Plant Methods.2017, 13:108
Curr Issues Mol Biol.2022, 44(10):5106-5116.
Drug Dev Res.2020, doi: 10.1002
Analytical Methods2018, 10(27)
Molecular & Cellular Toxicology2017, 13(3):271-278
Int J Mol Sci.2020, 21(9):3239.
South African J of Plant&Soil2018, 29-32
Phytomedicine.2024, 129:155645.
Chem Res Toxicol. 2022, acs.chemrestox.2c00049.
Related and Featured Products
Oncol Lett. 2015 Feb;9(2):897-902.
Ursolic acid inhibits the invasive phenotype of SNU-484 human gastric cancer cells.[Pubmed:
25621065]
Metastasis is a major cause of cancer-related mortality in patients with gastric cancer. Ursolic acid, a pentacyclic triterpenoid compound derived from medicinal herbs, has been demonstrated to exert anticancer effects in various cancer cell systems. However, to the best of our knowledge, the inhibitory effect of Ursolic acid on the invasive phenotype of gastric cancer cells has yet to be reported. Therefore, the aim of the present study was to investigate the effect of Ursolic acid on the invasiveness of SNU-484 human gastric cancer cells.
METHODS AND RESULTS:
Ursolic acid efficiently induced apoptosis, possibly via the downregulation of B-cell lymphoma 2 (Bcl-2), the upregulation of Bcl-2-associated X protein and the proteolytic activation of caspase-3. Furthermore, the activation of p38 mitogen-activated protein kinase and c-Jun N-terminal kinase was increased by the administration of Ursolic acid. In addition, Ursolic acid significantly suppressed the invasive phenotype of the SNU-484 cells and significantly decreased the expression of matrix metalloproteinase (MMP)-2, indicating that MMP-2 may be responsible for the anti-invasive activity of Ursolic acid.
CONCLUSIONS:
Taken together, the results of the present study demonstrate that Ursolic acid induces apoptosis and inhibits the invasive phenotype of gastric cancer cells; therefore, Ursolic acid may have a potential application as a chemopreventive agent to prevent the metastasis of gastric cancer or to alleviate the process of metastasis.
Eur J Pharmacol. 2015 Jul 5;758:171-6.
Anxiolytic-like effects of ursolic acid in mice.[Pubmed:
25861934]
Ursolic acid is a pentacyclic triterpenoid that possesses several biological and neuropharmacological effects including antidepressant-like activity. Anxiety disorders represent common and disability psychiatric conditions that are often associated with depressive symptoms.
METHODS AND RESULTS:
This work investigated the anxiolytic-like effects of Ursolic acid administration in different behavioral paradigms that evaluate anxiety in mice: open field test, elevated plus maze test, light/dark box test and marble burying test. To this end, mice were administered with Ursolic acid (0.1, 1 and 10mg/kg, p.o.) or diazepam (2mg/kg, p.o.), positive control, and submitted to the behavioral tests. The results show that Ursolic acid (10mg/kg) elicited an anxiolytic-like effect observed by the increased total time in the center and decreased number of rearings responses in the open field test and an increased percentage of entries and total time spent in the open arms of elevated plus maze, similarly to diazepam. No significant effects of Ursolic acid were shown in the light/dark box and marble burying test.
CONCLUSIONS:
These data indicate that Ursolic acid exhibits anxiolytic-like effects in the open field and elevated plus maze test, but not in the light/dark box and marble burying test, showing the relevance of testing several behavioral paradigms in the evaluation of anxiolytic-like actions. Of note, the results extend the understanding on the effects of Ursolic acid in the central nervous system and suggest that it may be a novel approach for the management of anxiety-related disorders.
Eur J Pharmacol. 2013 Feb 15;701(1-3):131-43.
Ursolic acid, a potential PPARγ agonist, suppresses ovalbumin-induced airway inflammation and Penh by down-regulating IL-5, IL-13, and IL-17 in a mouse model of allergic asthma.[Pubmed:
23201068 ]
Allergic asthma is a chronic airway disorder characterized by airway hyperresponsiveness to allergens, chronic airway inflammation, airway edema, increased mucus secretion, excess production of Th2 cytokines, and eosinophil accumulation in the lungs. Ursolic acid is known for its pharmacological effects, such as its anti-tumor, anti-inflammatory and antimicrobial activities. To investigate the anti-asthmatic effects and mechanism of Ursolic acid, we studied the development of pulmonary eosinophilic inflammation and enhanced pause (Penh) in a mouse model of allergic asthma.
METHODS AND RESULTS:
In this study, BALB/c mice were systemically sensitized to ovalbumin followed by intratracheal, intraperitoneal, and aerosol allergen challenges. We investigated the effect of Ursolic acid and Cyclosporin A (CsA) on Penh, pulmonary eosinophilic infiltration, various immune cell phenotypes, Th2 cytokines, IL-17 production, and ovalbumin specific IgE production in a mouse model of asthma. In BALB/c mice, Ursolic acid had suppressed eosinophil infiltration, allergic airway inflammation, and Penh, which occurred by suppressing the production of IL-5, IL-13, IL-17, and ovalbumin-specific IgE by blocking the GATA-3 and STAT6 pathways.
CONCLUSIONS:
Our data suggest the therapeutic mechanism of Ursolic acid in asthma is based on reductions of Th2 cytokines (IL-5 and IL-13), ovalbumin-specific IgE production, and eosinophil infiltration via the Th2-GATA-3, STAT6, and IL-17-NF-κB pathways.
Phytomedicine. 2003 Mar;10(2-3):115-21.
Cardiovascular, antihyperlipidemic and antioxidant effects of oleanolic and ursolic acids in experimental hypertension.[Pubmed:
12725563 ]
Cardiovascular (systolic and diastolic blood pressure, heart rate), antihyperlipidemic (tryglycerides, total cholesterol and lipoprotein fractions), antioxidant (glutathione peroxidase--GPx, and superoxide dismutase--SOD), diuretic/saluretic and hypoglycemic activity of 98% pure oleanolic acid(OA) and Ursolic acid(UA) were studied in Dahl salt-sensitive (DSS), insulin resistant rat model of genetic hypertension.
METHODS AND RESULTS:
Both OA and UA displayed low toxicity, with LC50 0.10 and 0.95 mg/ml, respectively. Although both triterpenoids did not have direct hypotensive effect, after 6-week application in a daily dose 60 mg/kg b.w., i.p., they prevented the development of severe hypertension. The antihypertensive effect was attributed to their potent diuretic-natriuretic-saluretic activity; direct cardiac effect (heart rate decrease by 34% and 32%, respectively); antihyperlipidemic (more than two times decrease of LDL and triglycerides); antioxidant (GPx increase by 12% and 10%, respectively; SOD increase by 12% and 22%, respectively), and hypoglycemic (blood glucose decrease by 20% and 50%, respectively) effects on the DSS rats.
CONCLUSIONS:
Except for the antihyperlipidemic effects, the other described above in vivo antihypertensive effects of OA and UA are reported for the first time and the underlying mechanisms are currently under investigation.
J Agric Food Chem. 2014 Oct 8;62(40):9711-21.
Ursolic acid isolated from the seed of Cornus officinalis ameliorates colitis in mice by inhibiting the binding of lipopolysaccharide to Toll-like receptor 4 on macrophages.[Pubmed:
25213465]
Ursolic acid, which was isolated from an ethanol extract of Cornus officinalis seed, potently inhibited nuclear factor κ light-chain enhancer of activated B cells (NF-κB) activation in lipopolysaccharide (LPS)-stimulated peritoneal macrophages.
METHODS AND RESULTS:
Therefore, we investigated the anti-inflammatory mechanism of Ursolic acid in LPS-stimulated macrophages and colitic mice. Ursolic acid inhibited phosphorylation of interleukin 1 receptor-associated kinase (IRAK)1, TAK1, inhibitor of nuclear factor κB kinase subunit β (IKKβ), and IκBα as well as activation of NF-κB and MAPKs in LPS-stimulated macrophages. Ursolic acid suppressed LPS-stimulated interleukin (IL)-1β, IL-6, tumor necrosis factor (TNF)-α, cyclooxygenase (COX)-2, and inducible NO synthetase (iNOS) expression as well as PGE2 and NO levels. Ursolic acid not only inhibited the Alexa Fluor 488-conjugated LPS-mediated shift of macrophages but also reduced the intensity of fluorescent LPS bound to the macrophages transiently transfected with or without MyD88 siRNA. However, Ursolic acid did not suppress NF-κB activation in peptidoglycan-stimulated macrophages. Oral administration of Ursolic acid significantly inhibited 2,4,6-trinitrobenzenesulfonic acid (TNBS)-induced colon shortening and myeloperoxidase (MPO) activity in mice. Ursolic acid also suppressed TNBS-induced COX-2 and iNOS expression as well as NF-κB activation in colon tissues. Ursolic acid (20 mg/kg) also inhibited TNBS-induced IL-1β, IL-6, TNF-α by 93, 86, and 85%, respectively (p < 0.05). However, Ursolic acid reversed TNBS-mediated downregulation of IL-10 expression to 79% of the normal control group (p < 0.05).
CONCLUSIONS:
On the basis of these findings, Ursolic acid may ameliorate colitis by regulating NF-κB and MAPK signaling pathways via the inhibition of LPS binding to TLR4 on immune cells.
Zhonghua Xue Ye Xue Za Zhi. 2015 Feb;36(2):153-7.
Effect of ursolic acid on proliferation of T lymphoma cell lines Hut-78 cells and its mechanism[Pubmed:
25778894]
To investigate the effects of Ursolic acid on T cell lymphoma cell lines-Hut-78 cells and its mechanism.
METHODS AND RESULTS:
Inhibition of Hut-78 cells proliferation by Ursolic acid at different concentration (10, 20, 40 and 80 μmol/L) for different incubation time (4, 12, 24, 48 and 72 h)was examined by MTT method, and early apoptosis by flow cytometry. The protein expressions of p65, p50, p52 and p100, and caspase-8, caspase-3 and caspase-9 were detected by Western blot. VEGF and COX-2 mRNA expressions were measured by reverse transcription polymerase chain reaction (RT-PCR).
It was showed that Ursolic acid inhibited proliferation of Hut-78 cells (P<0.05). Apoptosis of Hut-78 cells was induced by 10, 20, 40 and 80 μmol/L Ursolic acid treatment (P<0.01). Likewise, expression of p65 and p50 proteins were down-regulated by Ursolic acid treatment (10, 20, 40 and 80 μmol/L) (P<0.01), but there was no significant change in the expression of p52 and p100. Moreover, Ursolic acid could up-regulate expression of caspase-8, caspase-3 and caspase-9 protein (P<0.01). RT-PCR examination showed that VEGF and COX-2 mRNA expression decreased by Ursolic acid treatment.
CONCLUSIONS:
Inhibition of Hut-78 cells proliferation may be related to Ursolic acid induced apoptosis through h death receptors and mitochondrial pathways. NF-κB classical signal pathway may be one of its mechanisms, and VEGF and cox-2 may also be involved.
Clin Res Hepatol Gastroenterol. 2015 Apr;39(2):188-97.
Protective effects of ursolic acid in an experimental model of liver fibrosis through Nrf2/ARE pathway.[Pubmed:
25459994]
Liver fibrosis is a reversible wound-healing response that occurs following liver injury. In this study, we aimed to investigate the possible protective effects of Ursolic acid in liver fibrosis induced by carbon tetrachloride (CCl4).
METHODS AND RESULTS:
ICR mice were randomly divided into six groups (Group 1: normal; Group 2: CCl4-treated group; Group 3: CCl4 plus Ursolic acid 25mg/kg group; Group 4: CCl4 plus Ursolic acid 50mg/kg group; Group 5: CCl4 plus colchicine 1mg/kg group; Group 6: Ursolic acid 50mg/kg group). Mice were administered with CCl4 (2 mL of CCl4 in olive oil (1:1, v/v) per kg body weight twice weekly) by intraperitoneal injection and oral injection of colchicine (1mg/kg) or Ursolic acid (25, 50mg/kg) daily. After six weeks, serum aminotransferase activity, hepatic reactive oxygen species (ROS) production, thiobarbituric acid reactive substances (TBARS), antioxidase (SOD, CAT, GPx) activity and histopathological analysis were performed. The levels of nuclear factor E2-related factor 2 (Nrf2), NAD(P)H: quinone oxidoreductase-1 (NQO1), glutathione S-transferase (GST) and heme oxygenase-1 (HO-1), tumor necrosis factor-alpha (TNF-α), prostaglandin E2 (PGE2) and inducible nitric oxide synthase (iNOS), Bcl-2 and caspase-3 were measured.
Ursolic acid significantly prevented CCl4-induced hepatotoxicity and fibrosis, indicated by both diagnostic indicators and histopathological analysis. CCl4-induced profound elevations of oxidative stress, inflammation and apoptosis in liver were suppressed by Ursolic acid.
CONCLUSIONS:
These results suggest that Ursolic acid has the hepatoprotective actions. The inhibition of CCl4-induced liver fibrosis, inflammation and apoptosis by Ursolic acid is due at least in part to its ability to modulate the Nrf2/ARE signalling pathway.
Biochem Pharmacol. 2007 Oct 1;74(7):1078-90.
Ursolic acid ameliorates cognition deficits and attenuates oxidative damage in the brain of senescent mice induced by D-galactose.[Pubmed:
17692828]
Ursolic acid (UA), a pentracyclic triterpene, is reported to have an antioxidant activity. Here we assessed the protective effect of UA against the d-galactose (D-gal)-induced neurotoxicity.
METHODS AND RESULTS:
We found that UA markedly reversed the D-gal induced learning and memory impairment by behavioral tests. The following antioxidant defense enzymes were measured: superoxide dismutases (SOD), catalase (CAT), glutathione peroxidase (GPx) and glutathione reductase (GR). The content of the lipid peroxidation product malondialdehyde (MDA) was also analyzed. Our results indicated that the neuroprotective effect of UA against D-gal induced neurotoxicity might be caused, at least in part, by the increase in the activity of antioxidant enzymes with a reduction in lipid peroxidation. And UA also inhibited the activation of caspase-3 induced by D-gal. Furthermore, we found that UA significantly increased the level of growth-associated protein GAP43 in the brain of D-gal-treated mice.
CONCLUSIONS:
These results suggest that the pharmacological action of UA may offer a novel therapeutic strategy for the treatment of age-related conditions.