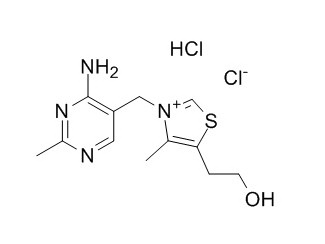
Thiamine hydrochloride
Thiamine hydrochloride is an efficient catalyst for the synthesis of amidoalkyl naphthols, it has prophylactic potential on lead induced lipid peroxidation in rat liver and kidney. Thiamine hydrochloride complex as a new anti-diabetic candidate.
Inquire / Order:
manager@chemfaces.com
Technical Inquiries:
service@chemfaces.com
Tel:
+86-27-84237783
Fax:
+86-27-84254680
Address:
1 Building, No. 83, CheCheng Rd., Wuhan Economic and Technological Development Zone, Wuhan, Hubei 430056, PRC
Providing storage is as stated on the product vial and the vial is kept tightly sealed, the product can be stored for up to
24 months(2-8C).
Wherever possible, you should prepare and use solutions on the same day. However, if you need to make up stock solutions in advance, we recommend that you store the solution as aliquots in tightly sealed vials at -20C. Generally, these will be useable for up to two weeks. Before use, and prior to opening the vial we recommend that you allow your product to equilibrate to room temperature for at least 1 hour.
Need more advice on solubility, usage and handling? Please email to: service@chemfaces.com
The packaging of the product may have turned upside down during transportation, resulting in the natural compounds adhering to the neck or cap of the vial. take the vial out of its packaging and gently shake to let the compounds fall to the bottom of the vial. for liquid products, centrifuge at 200-500 RPM to gather the liquid at the bottom of the vial. try to avoid loss or contamination during handling.
Food and Agriculture Org. Of the UN2019, 151-160
J Cachexia Sarcopenia Muscle.2022, 13(6):3149-3162.
J Agric Food Chem.2018, 66(1):351-358
Exp Mol Med.2020, 52(4):629-642.
Molecules.2023, 28(13):4971.
Phytomedicine.2024, 125:155350.
J Vet Sci.2020, 21(3):e39.
bioRxiv - Molecular Biology2023, 535548.
J Pharm Biomed Anal.2024, 251:116444.
Korean J. Medicinal Crop Sci.2022, 30(2):117-123.
Related and Featured Products
Nahrung. 2002 Aug;46(4):256-7.
Effect of thiamine hydrochloride, pyridoxine hydrochloride and calcium-d-pantothenate on the patulin content of apple juice concentrate.[Pubmed:
12224421]
Thiamine hydrochloride, pyridoxine hydrochloride and calcium-d-pantothenate were applied apple juice concentrates (AJC) at various doses in order to reduce the patulin content.
METHODS AND RESULTS:
AJC samples containing high levels of patulin were stored at 22 +/- 2 degrees C and 4 degrees C for 6 months after vitamins were added. Patulin was fully degraded at the end of a 6-month period in samples stored at 22 +/- 2 degrees C, on the other hand, other quality parameters diminished significantly. Without any considerable reduction on other quality parameters, applications of 1000 and 2500 mg/kg calcium-d-pantothenate resulted in reduction of patulin of 73.6 and 94.3%, respectively, however, 42.1% of patulin reduction was observed in the control sample of AJC stored for 1 month at 22 +/- 2 degrees C. Addition of Thiamine hydrochloride (1000 mg/kg), pyrodoxine hydrochloride (625 or 875 mg/kg) and calcium-d-pantothenate (1000 or 2500 mg/kg) into the samples and storage at 4 degrees C for 6 months yielded 55.5 to 67.7% of patulin reduction which was only 35.8% for the control while the other quality parameters were protected adequately.
J Clin Pharmacol. 2014 Jun;54(6):688-95.
Pharmacokinetic study of benfotiamine and the bioavailability assessment compared to thiamine hydrochloride.[Pubmed:
24399744]
Benfotiamine is a lipid-soluble thiamine precursor which can transform to thiamine in vivo and subsequently be metabolized to thiamine monophosphate (TMP) and thiamine diphosphate (TDP).
METHODS AND RESULTS:
This study investigated the pharmacokinetic profiles of thiamine and its phosphorylated metabolites after single- and multiple-dose administration of benfotiamine in healthy Chinese volunteers, and assessed the bioavailability of orally benfotiamine administration compared to Thiamine hydrochloride. Compared to Thiamine hydrochloride, the bioavailability of thiamine in plasma and TDP in erythrocyte after oral administration of benfotiamine were 1147.3 ± 490.3% and 195.8 ± 33.8%, respectively.
METHODS AND RESULTS:
The absorption rate and extent of benfotiamine systemic availability of thiamine were significantly increased indicating higher bioavailability of thiamine from oral dose of benfotiamine compared to oral dose of Thiamine hydrochloride.
Int J Immunopathol Pharmacol. 2015 Mar 26.
Synthesis, characterization, and efficacy evaluation of a new anti-diabetic vanadyl(II) thiamine hydrochloride complex in streptozotocin-induced diabetic rats.[Pubmed:
25816395]
Diabetes mellitus (DM) is a chronic metabolic disorder characterized by hyperglycemia due to abnormalities in either insulin secretion or action. A range of vanadium complexes have been synthesized and demonstrated to be effective in lowering hyperglycemia. Thiamine administration was also reported to prevent deterioration in fasting glucose and insulin levels, and to improve glucose tolerance in hyperglycemic patients.
METHODS AND RESULTS:
This study has been conducted to evaluate the ionic vanadyl(II) Thiamine hydrochloride complex (VC) as a new anti-diabetic candidate. The new complex was characterized by infrared spectroscopy (FT-IR), electronic spectra, magnetic susceptibility, electron spin resonance (ESR), scanning electron microscopy (SEM), and thermogravimetric analysis (TGA). The anti-diabetic effect of VC was investigated in comparison to vanadium sulfate in streptozotocin (STZ)-induced diabetic rats. Treatment of diabetic rats with VC versus vanadyl sulfate showed a more potent effect on reducing serum glucose and cholesterol close to normal levels. VC suppressed the diabetes-induced upregulation of hepatic glucose transporter (GLUT)-2, Phosphoenol pyruvate carboxykinase (PEPCK), and hormone-sensitive lipase (HSL) more significantly than vanadyl sulfate. Either vanadyl sulfate or VC restored hepatic sterol regulatory element-binding protein transcription factor-1c (SREBP-1c) and muscle hexokinase (HK) mRNA expression that was downregulated in diabetic group. Pyruvate kinase (PK) mRNA expression was restored more significantly in VC-treated than vanadyl sulfate-treated diabetic rats.
CONCLUSIONS:
These results indicate that the newly synthesized VC could be an effective anti-diabetic candidate as the anti-diabetic activity of the ionic vanadium was enhanced after being modified with the organic ligand, thiamin. The results also suggest that VC achieves its effect most likely through modulating the transcription of energy metabolizing enzymes.
Vet Hum Toxicol. 2000 Aug;42(4):236-7.
Effect of thiamine hydrochloride on lead induced lipid peroxidation in rat liver and kidney.[Pubmed:
10928693]
METHODS AND RESULTS:
Thiamine hydrochloride was studied on lead-induced endogenous lipid peroxidation in rat hepatic and renal tissues following po doses of 2.73 mg lead/kg bw for 6 w. Simultaneous use of 25 mg Thiamine hydrochloride/kg bw po reduced lead accumulation in liver and kidneys. There were significant decreases in endogenous lipid peroxide in liver and kidney from Thiamine hydrochloride-treated rats. Histopathological lesions in thiamine-treated livers and kidneys were milder in comparison to lesions in untreated Pb-exposed animals.
CONCLUSIONS:
This indicates the prophylactic potential of thiamine for lead-induced lipid peroxidation.
Tetrahedron Letters, 2009, 50(46):6393-6397.
Thiamine Hydrochloride as an Efficient Catalyst for the Synthesis of Amidoalkyl Naphthols.[Reference:
WebLink]
A simple, efficient, and practical procedure for the synthesis of amidoalkyl naphthols using Thiamine hydrochloride (VB1) as a novel catalyst is described in high yields. The salient features of the catalyst are efficiency, inexpensiveness, non-toxicity, and metal ion free.