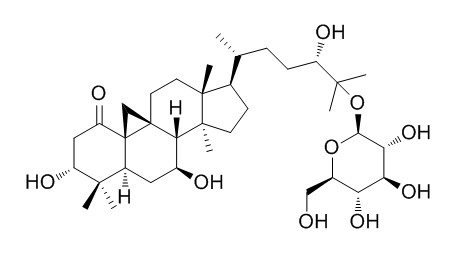
Sutherlandioside B
Sutherlandioside B and Sutherlandia frutescens exhibit dissociated glucocorticoid characteristics underline potential therapeutic applications in the treatment of inflammation and hypertension.
Inquire / Order:
manager@chemfaces.com
Technical Inquiries:
service@chemfaces.com
Tel:
+86-27-84237783
Fax:
+86-27-84254680
Address:
1 Building, No. 83, CheCheng Rd., Wuhan Economic and Technological Development Zone, Wuhan, Hubei 430056, PRC
Providing storage is as stated on the product vial and the vial is kept tightly sealed, the product can be stored for up to
24 months(2-8C).
Wherever possible, you should prepare and use solutions on the same day. However, if you need to make up stock solutions in advance, we recommend that you store the solution as aliquots in tightly sealed vials at -20C. Generally, these will be useable for up to two weeks. Before use, and prior to opening the vial we recommend that you allow your product to equilibrate to room temperature for at least 1 hour.
Need more advice on solubility, usage and handling? Please email to: service@chemfaces.com
The packaging of the product may have turned upside down during transportation, resulting in the natural compounds adhering to the neck or cap of the vial. take the vial out of its packaging and gently shake to let the compounds fall to the bottom of the vial. for liquid products, centrifuge at 200-500 RPM to gather the liquid at the bottom of the vial. try to avoid loss or contamination during handling.
Antiviral Res.2013, 98(3):386-93
Molecules.2019, 24(11):E2044
Journal of Apicultural Research2021, 60(1).
Pharmaceuticals (Basel).2021, 14(10):1046.
Cell Mol Biol(Noisy-le-grand)2019, 65(7):77-83
Food Chem Toxicol.2023, 176:113785.
Int J Mol Sci.2023, 25(1):162.
BMC Complement Altern Med.2018, 18(1):221
J of Engineering Science&Technology2018, 13(9):2820-2828
Biochem Biophys Res Commun.2018, 495(1):1271-1277
Related and Featured Products
Journal of ethnopharmacology, 2017, 202.
Sutherlandia frutescens modulates adrenal hormone biosynthesis, displays anti-mineralocorticoid and SERGA properties acting as a dissociated glucocorticoid.[Reference:
WebLink]
Ethnopharmacological relevance: Sutherlandia frutescens is a traditional African medicinal plant used in the treatment of stress and anxiety, while also exhibiting anti-inflammatory properties. The study aimed at linking anti-stress and anti-inflammatory properties of S. frutescens to its influence on glucocorticoid biosynthesis and the inflammatory response via steroid receptor interaction.
METHODS AND RESULTS:
The influence of S. frutescens extracts and Sutherlandioside B (SUB),10 and 30µM, on key steroidogenic enzymes was assayed in COS-1 cells. Effects were also assayed on basal and stimulated hormone levels in the adrenal H295R cell model. Agonist activity for transactivation and transrepression of the extract and SUB with the glucocorticoid- (GR) and mineralocorticoid receptor (MR) was subsequently investigated. Inhibitory effects of the extract towards progesterone conversion by CYP17A1 and CYP21A2 were significant. SUB inhibited CYP17A1 and 3β-HSD2, while not affecting CYP21A2. In H295R cells, SUB decreased cortisol and androgen precursors significantly. The extract decreased total steroid production (basal and stimulated) with cortisol and its precursor, deoxycortisol, together with mineralocorticoid metabolites significantly decreased under forskolin stimulated conditions. S. frutescens extracts and SUB repressed NF-κB-driven gene expression without activating GRE-driven gene expression and while neither activated MR mediated gene transcription, both antagonized the effects of aldosterone via the MR.
CONCLUSIONS:
Data provide evidence linking anti-stress, anti-inflammatory and anti-hypertensive properties of S. frutescens to inhibition of steroidogenic enzymes and modulation of adrenal hormone biosynthesis. Findings suggesting S. frutescens and SUB exhibit dissociated glucocorticoid characteristics underline potential therapeutic applications in the treatment of inflammation and hypertension.
Planta Medica, 2009, 75(04):s-2009-1216513.
Quantitative Determination of Cycloartane and Flavonoid Glycosides from Sutherlandia frutescens by UPLC-UV, UPLC-ELSD Methods and Confirmation by UPLC-MS.[Reference:
WebLink]
METHODS AND RESULTS:
Sutherlandia frutescens (L.) R. BR., Family Fabaceae, is a well-known and widely used medicinal plant from the Western Cape, South Africa [1,2]. Traditionally it has been used as a remedy for stomach problems, internal cancers, diabetes and various inflammatory conditions. Recently, it has been used for the management of HIV/AIDS in patients [1]. This paper describes the analytical method suitable for the determination of four flavonoid glycosides (Sutherlandin A, B, C, D) and four cycloartane glycosides (Sutherlandioside A, Sutherlandioside B, Sutherlandioside C, Sutherlandioside D) from stem-leaves of Sutherlandia frutescens (L.) R. BR. A separation by UPLC was achieved by using Acquity shield RP18 column, PDA with ELS detection, and a water/acetonitrile gradient as the mobile phase. The major cycloartane glycoside compound (Sutherlandioside B) was detected at a concentration as low as 1.0 µg/mL. The analysis of plant material and products showed considerable variation of 0.6–2.7% for the major compound. This method involved the use of the [M+H]+ and [M+Na]+ ions in the positive ion mode with extractive ion monitoring (EIM).
CONCLUSIONS:
The eight compounds were further confirmed by UPLC-MS method in plant sample and products. In the positive ion mode, the protonated species [M+H]+ at m/z 741.2, 741.2, 725.2, 725.2, 653.4, 651.4, 635.4 and 653.4 and sodiated species [M+Na]+ at m/z 763.2, 763.2, 747.2, 747.2, 675.4, 673.4, 657.4 and 675.4 for compounds 1–8 were observed.