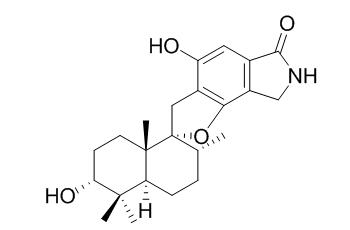
Stachybotrylactam
Stachybotrylactam has toxicity.
Inquire / Order:
manager@chemfaces.com
Technical Inquiries:
service@chemfaces.com
Tel:
+86-27-84237783
Fax:
+86-27-84254680
Address:
1 Building, No. 83, CheCheng Rd., Wuhan Economic and Technological Development Zone, Wuhan, Hubei 430056, PRC
Providing storage is as stated on the product vial and the vial is kept tightly sealed, the product can be stored for up to
24 months(2-8C).
Wherever possible, you should prepare and use solutions on the same day. However, if you need to make up stock solutions in advance, we recommend that you store the solution as aliquots in tightly sealed vials at -20C. Generally, these will be useable for up to two weeks. Before use, and prior to opening the vial we recommend that you allow your product to equilibrate to room temperature for at least 1 hour.
Need more advice on solubility, usage and handling? Please email to: service@chemfaces.com
The packaging of the product may have turned upside down during transportation, resulting in the natural compounds adhering to the neck or cap of the vial. take the vial out of its packaging and gently shake to let the compounds fall to the bottom of the vial. for liquid products, centrifuge at 200-500 RPM to gather the liquid at the bottom of the vial. try to avoid loss or contamination during handling.
Food Engineering Progress2019, 23(3)209-216
BMC Plant Biol.2022, 22(1):128.
J Mol Med (Berl).2018, 96(7):661-672
J of Health Science and Alternative Medicine2019, 1(1)
Plant Physiol Biochem.2019, 144:355-364
Nat Chem Biol.2018, 14(8):760-763
World J Mens Health.2019, 10.5534
Nutrients.2021, 13(12):4364.
Int Immunopharmacol.2019, 71:22-31
Daru.2022, 30(2):273-288.
Related and Featured Products
Indoor & Built Environment, 2010, 19(19):668-675.
A study of the toxicity of moulds isolated from dwellings.[Reference:
WebLink]
METHODS AND RESULTS:
An analysis of the toxicity of moulds isolated from 34 dwellings with mould-affected walls was performed. During the analysis 74 moulds strains were isolated, 17.5% of them were toxic. Detailed analysis by high performance liquid chromatography/tandem mass spectrometry of six toxic strains proved their ability to grow on building materials and produce mycotoxins. It was confirmed that the toxins Stachybotrylactam, sterigmatocystin and roquefortin were produced on gypsum board and concrete by Stachybotrys chartarum, Aspergillus versicolor and Penicillium chrysogenum, respectively. This is also the first report on the production of aflatoxin B1 and G1 by A. flavus on building materials. Extracts from A. versicolor, A. flavus, P. chrysogenum growing on building materials were found to have cytotoxic potential.
CONCLUSIONS:
It was found that some mycotoxin production may be reduced or may even vanish, when moulds grow on building materials. However, taking into consideration the appreciable amounts of some mycotoxins that were still produced on the building materials investigated, the study indicated a toxic risk in the mould-affected buildings analysed.
Mar Drugs. 2014 Apr 1;12(4):1924-38.
Spirocyclic drimanes from the marine fungus Stachybotrys sp. strain MF347.[Pubmed:
24694571 ]
METHODS AND RESULTS:
A novel spirocyclic drimane coupled by two drimane fragment building blocks 2 and a new drimane 1 were identified in mycelia and culture broth of Stachybotrys sp. MF347. Their structures were established by spectroscopic means. This is the first example of spirocyclic drimane coupled by a spirodihydrobenzofuranlactam unit and a spirodihydroisobenzofuran unit; and the connecting position being N-C instead of an N and N connecting unit. Strain MF347 produced also the known spirocyclic drimanes stachybocin A (12) and stachybocin B (11) featured by two sesquiterpene-spirobenzofuran structural units connected by a lysine residue; the known spirocyclic drimanes chartarlactam O (5); chartarlactam K (6); F1839A (7); Stachybotrylactam (8); stachybotramide (9); and 2α-acetoxyStachybotrylactam acetate (10); as well as ilicicolin B (13), a known sesquiterpene. The relative configuration of two known spirobenzofuranlactams (3 and 4) was determined.
CONCLUSIONS:
All compounds were subjected to biological activity tests. The spirocyclic drimane 2, 11, and 12, as well as the sesquiterpene 13, exhibited antibacterial activity against the clinically relevant methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus (MRSA).