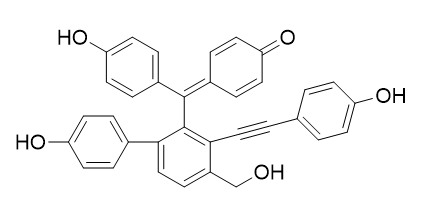
Selaginellin
Selaginellin has a neuroprotective effect against L-glutamate-induced neurotoxicity through mechanisms related to anti-oxidation and anti-apoptosis via scavenging reactive oxygen species and up-regulating the expression of klotho gene. Selaginellin shows inhibitory effect on high glucose-induced cell injury and apoptosis in differentiated PC12 cells, which is related to inhibition of LOX-1/NADPH oxidase-reactive oxygen species/caspase-3 signaling pathway.
Inquire / Order:
manager@chemfaces.com
Technical Inquiries:
service@chemfaces.com
Tel:
+86-27-84237783
Fax:
+86-27-84254680
Address:
1 Building, No. 83, CheCheng Rd., Wuhan Economic and Technological Development Zone, Wuhan, Hubei 430056, PRC
Providing storage is as stated on the product vial and the vial is kept tightly sealed, the product can be stored for up to
24 months(2-8C).
Wherever possible, you should prepare and use solutions on the same day. However, if you need to make up stock solutions in advance, we recommend that you store the solution as aliquots in tightly sealed vials at -20C. Generally, these will be useable for up to two weeks. Before use, and prior to opening the vial we recommend that you allow your product to equilibrate to room temperature for at least 1 hour.
Need more advice on solubility, usage and handling? Please email to: service@chemfaces.com
The packaging of the product may have turned upside down during transportation, resulting in the natural compounds adhering to the neck or cap of the vial. take the vial out of its packaging and gently shake to let the compounds fall to the bottom of the vial. for liquid products, centrifuge at 200-500 RPM to gather the liquid at the bottom of the vial. try to avoid loss or contamination during handling.
Biofactors.2018, 44(2):168-179
Molecules.2023, 28(16):6025.
Onco Targets Ther.2017, 10:3467-3474
Heliyon.2023, e12684.
Foods.2023, 12(6):1227.
Food Research International2023, 113792.
Eur J Pharmacol.2023, 950:175772.
Molecules.2019, 24(4):E744
The Journal of Supercritical Fluids2021, 176:105305.
Chem Biol Interact.2019, 315:108910
Related and Featured Products
Naunyn Schmiedebergs Arch Pharmacol. 2010 Jan;381(1):73-81.
Protective effect of selaginellin on glutamate-induced cytotoxicity and apoptosis in differentiated PC12 cells.[Pubmed:
19936711 ]
L-glutamate plays a key role in neuronal cell death associated with many neurodegenerative conditions such as cerebral ischemia, hypoxia, Alzheimer's, Huntington's, and Parkinson's diseases.
METHODS AND RESULTS:
Selaginellin, a component extracted from Saussurea pulvinata (Hook.et Grev.) Maximo, was assessed for its ability to protect rat pheochromocytoma (PC12) cells against oxidative toxicity induced by glutamate. The differentiated PC12 cells were pretreated with various concentrations (10(-7), 3 x 10(-7), or 10(-6) M) of Selaginellin for 1 h prior to exposure to L-glutamate. Selaginellin was shown to protect PC12 cells against glutamate toxicity, as determined by characteristic morphological features, lactate dehydrogenase release and cell viability, and apoptosis as evaluated by Hoechst 33342 staining assay and caspase-3 activity. In addition, the increase in levels of reactive oxygen species and decrease in klotho gene expression induced by glutamate were significantly reversed by Selaginellin.
CONCLUSIONS:
Our study suggests that Selaginellin has a neuroprotective effect against L-glutamate-induced neurotoxicity through mechanisms related to anti-oxidation and anti-apoptosis via scavenging reactive oxygen species and up-regulating the expression of klotho gene.
Eur J Pharmacol. 2012 Nov 5;694(1-3):60-8.
Inhibitory effect of selaginellin on high glucose-induced apoptosis in differentiated PC12 cells: role of NADPH oxidase and LOX-1.[Pubmed:
22964466 ]
Hyperglycemia clearly plays a key role in the development and progression of diabetic neuropathy. Hyperglycemia induces oxidative stress to generate reactive oxygen species in diabetic neurons resulting in neuronal damage and dysfunction.Apoptosis has been proposed as a possible mechanism for high glucose-induced neural dysfunction and neuronal cell injury.
METHODS AND RESULTS:
High glucose per se enhances lectin-like oxidized low density lipoprotein receptor-1 (LOX-1) expression via activation of NADPH oxidase/reactive oxygen species pathway in endothelial cells. Selaginellin, a component extracted from Saussurea pulvinata (Hook. et Grev.) Maxim, was assessed for its ability to protect rat pheochromocytoma (PC12) cells against oxidative toxicity induced by high glucose. The differentiated PC12 cells were pretreated with various concentrations (10(-7), 3×10(-7) or 10(-6) M) of Selaginellin for 1 h and then co-treated with Selaginellin and D-glucose (75 mM) for 72 h. Selaginellin was shown to protect differentiated PC12 cells against high glucose toxicity, as determined by characteristic morphological features, cell viability, and apoptosis as evaluated by Hoechst 33,258 staining assay, annexin V-propidium iodide double staining assay and caspase-3 activity. In addition, the increase in NADPH oxidase activity, mRNA expression of NADPH oxidase subunits (NOX-1 and NOX-2) and LOX-1, and reactive oxygen species production induced by high glucose were significantly inhibited by Selaginellin or by anti-LOX-1 antibody.
CONCLUSIONS:
The present study demonstrated that inhibitory effect of Selaginellin on high glucose-induced cell injury and apoptosis in differentiated PC12 cells is related to inhibition of LOX-1/NADPH oxidase-reactive oxygen species/caspase-3 signaling pathway.