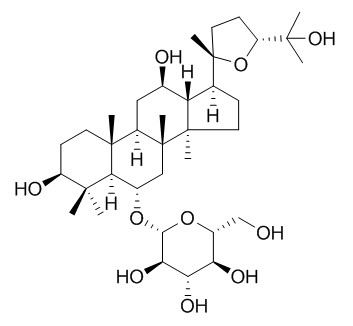
Pseudoginsenoside RT5
Pseudoginsenoside RT5 is a nartural product from Panax ginseng C. A. Mey.
Inquire / Order:
manager@chemfaces.com
Technical Inquiries:
service@chemfaces.com
Tel:
+86-27-84237783
Fax:
+86-27-84254680
Address:
1 Building, No. 83, CheCheng Rd., Wuhan Economic and Technological Development Zone, Wuhan, Hubei 430056, PRC
Providing storage is as stated on the product vial and the vial is kept tightly sealed, the product can be stored for up to
24 months(2-8C).
Wherever possible, you should prepare and use solutions on the same day. However, if you need to make up stock solutions in advance, we recommend that you store the solution as aliquots in tightly sealed vials at -20C. Generally, these will be useable for up to two weeks. Before use, and prior to opening the vial we recommend that you allow your product to equilibrate to room temperature for at least 1 hour.
Need more advice on solubility, usage and handling? Please email to: service@chemfaces.com
The packaging of the product may have turned upside down during transportation, resulting in the natural compounds adhering to the neck or cap of the vial. take the vial out of its packaging and gently shake to let the compounds fall to the bottom of the vial. for liquid products, centrifuge at 200-500 RPM to gather the liquid at the bottom of the vial. try to avoid loss or contamination during handling.
Sains Malaysiana2024, 53(4):795-805
Journal of Third Military Medical University2019, 41(2):110-115
J Microbiol Biotechnol.2022, 32(2):141-148.
Plant Cell,Tissue & Organ Culture2016, 127(1):115-121
Molecules.2020, 25(21):5087.
Food Sci Biotechnol.2024, 34(3):611-620.
Nutrients.2023, 15(6):1417.
Phytochem Anal.2016, 27(5):296-303
Hum Exp Toxicol.2017, 36(11):1169-1176
Biomolecules.2020, 10(6):925.
Related and Featured Products
Zhong Yao Cai. 2014 Oct;37(10):1743-8.
Research on dynamic accumulation of nine ginsenosides and two pseudo-ginsenosides of Panax quinquefolium root of different growth years and harvest months in Canada.[Pubmed:
25895377]
RP-HPLC-ELSD was adopted. The analysis was performed on a Dimaonsil C18 (250 mm x 4.6 mm, 5 μm) column, the mobile phase was acetonitrile (A)-deionized water (B) in gradient elution mode.
METHODS AND RESULTS:
The flow rate was 1.0 mL/min and column temperature was set at 30 °C. The carrier gas was nitrogen with flow rate of 2.8 L/min, the drift tube temperature was 100 °C, and the injection volume was 10 μL. The principle component analysis and cluster analysis of SPSS software (version 19.0) were conducted for the data analysis. The RP-HPLC-ELSD method for determining simultaneously nine ginsenosides and two pseudoginsenosides was established. The total content of ginsenosides of one- to two-year-old was low and increased from May to September in each year. That of three- to five-year-old declined from June to July and increased from August, and was the highest in September of three- to five-year-old samples. The total content from September of three-year-old samples was similar. The content of nine ginsenosides and two pseudo-ginsenosides was relatively high in all the samples except ginsenoside Rc, which wasn't determined in some samples. The ginsenosides Rd, Rb3 and pseudo-ginsenoside F11 were higher than others. The principle component analysis results showed that ginsenosides Rg1, Re, Rb1, Rc, Rb2, Rb3, Rg3 and pseudoginsenoside F11,Pseudoginsenoside RT5 could be the characteristic ginsenosides of Panax quinquefolium root in Canada.
CONCLUSIONS:
The cluster analysis indicated that the chemical constituent and dynamic accumulation of ginsenosides of one- to two-year-old was similar except the sample of July of four-year-old and there was no obvious difference of three- to five-year-old.
Zhongguo Zhong Yao Za Zhi. 2003 Sep;28(9):830-3.
[Studies on saponin constituents in roots of Panax quinquefolium].[Pubmed:
15015374]
To examine the saponins constituents in roots of Panax quinquefolium cultivated in China.
METHODS AND RESULTS:
The methanol extract from roots of P. quinquefolium cultivated in Jiling province of China was extracted by chloroform and n-butanol successively. Ten pure saponins were isolated from the n-butanol extract by silica gel and RP-8 reversed-phase column chromatography. Their structures were identified by means of spectral methods and compared with known compounds.
Ten saponins were isolated from P. quinquefolium. They were identified as ginsenoside Rg1(2), Re(5), Rd(7), Rc(8), Rb1(9), Rb2(10), 24(R)-ginsenoside Rg3(3), 24(R)-Pseudoginsenoside RT5(1), F11(4) and notoginsenoside K(6), respectively.
CONCLUSIONS:
This work has elucidated the saponins constituents of P. quinquefolium cultivated in Jilin province of China and has shown that compound 1 was isolated from this plant for the first time.
5,7,2',4'-Tetrahydroxy-8,3'-di(gamma,gamma-dimethylallyl)-isoflavanone
Catalog No: CFN95084
CAS No: 141846-47-1
Price: $413/5mg
Orcinol 1-O-beta-D-apiofuranosyl-(1->6)-beta-D-glucopyranoside
Catalog No: CFN95109
CAS No: 868557-54-4
Price: $338/5mg
Silychristin B
Catalog No: CFN95160
CAS No: 879325-58-3
Price: $318/5mg
(1,5E,11E)-tridecatriene-7,9-diyne-3,4-diacetate
Catalog No: CFN95161
CAS No: 201012-14-8
Price: $318/10mg
Somnifericin
Catalog No: CFN95280
CAS No: 173693-57-7
Price: $318/5mg
Isosaponarin 2''-O-glucoside (Isovitexin-2''-4'-di-O-beta-D-glucoside)
Catalog No: CFN95296
CAS No: 63316-27-8
Price: $318/10mg
Moreollic acid
Catalog No: CFN95437
CAS No: 173792-68-2
Price: $318/5mg
2-(2,4-Dihydroxyphenyl)-5,6-methylenedioxybenzofuran (ABF)
Catalog No: CFN95511
CAS No: 67121-26-0
Price: $318/5mg
Scoparin
Catalog No: CFN95544
CAS No: 301-16-6
Price: $318/5mg
(Z)-Ferulic acid 4-O-beta-D-glucoside
Catalog No: CFN95546
CAS No: 94942-20-8
Price: $168/20mg