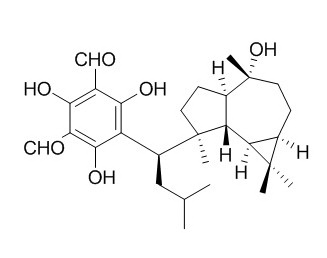
Macrocarpal A
Macrocarpal A is the key component that stimulates the synthesis of ceramide in the stratum corneum. Macrocarpal A has cytotoxic, and antibacterial activities.
Inquire / Order:
manager@chemfaces.com
Technical Inquiries:
service@chemfaces.com
Tel:
+86-27-84237783
Fax:
+86-27-84254680
Address:
1 Building, No. 83, CheCheng Rd., Wuhan Economic and Technological Development Zone, Wuhan, Hubei 430056, PRC
Providing storage is as stated on the product vial and the vial is kept tightly sealed, the product can be stored for up to
24 months(2-8C).
Wherever possible, you should prepare and use solutions on the same day. However, if you need to make up stock solutions in advance, we recommend that you store the solution as aliquots in tightly sealed vials at -20C. Generally, these will be useable for up to two weeks. Before use, and prior to opening the vial we recommend that you allow your product to equilibrate to room temperature for at least 1 hour.
Need more advice on solubility, usage and handling? Please email to: service@chemfaces.com
The packaging of the product may have turned upside down during transportation, resulting in the natural compounds adhering to the neck or cap of the vial. take the vial out of its packaging and gently shake to let the compounds fall to the bottom of the vial. for liquid products, centrifuge at 200-500 RPM to gather the liquid at the bottom of the vial. try to avoid loss or contamination during handling.
Eur J Pharmacol.2024, 981:176883.
Ind Crops Prod.2015, 67:185-191
J Health Sci Med Res.2023, 31584.
Daru.2024, 32(2):689-703.
Front. Physiol.2022, 790345.
The Thai Journal of Pharmaceutical Sciences2023, 47(3):3.
Food Res Int.2024, 191:114613.
Sci Rep.2023, 13(1):14594.
J Lipid Res.2024, 65(10):100640.
Antioxidants (Basel).2020, 9(11):1121.
Related and Featured Products
Sci Rep. 2014 Jul 2;4:5410.
Cytotoxic activity of acyl phloroglucinols isolated from the leaves of Eucalyptus cinerea F. Muell. ex Benth. cultivated in Egypt.[Pubmed:
24986654]
METHODS AND RESULTS:
Two acyl phloroglucinol compounds namely; Sideroxylonal B (1) and Macrocarpal A (2) were isolated from the Sideroxylonal-Rich Extract (SRE) of the juvenile leaves of Eucalyptus cinerea; F. Muell. ex Benth cultivated in Egypt.Meanwhile, the (SRE) together with (1) and (2) exhibited low cytotoxicity against normal cell line 10 FS, with IC₅₀ 55.4 ± 1.4, 43 ± 0.8 and 50.1 ± 1.12 μg mL-1, respectively. The antiprofilerative activity of the tested compounds was evaluated.
CONCLUSIONS:
The cell cycle profile of cells treated with Sideroxylonal-B and Macrocarpal-A indicates possible S-phase specific effects.
Int J Cosmet Sci. 2012 Feb;34(1):17-22.
Eucalyptus increases ceramide levels in keratinocytes and improves stratum corneum function.[Pubmed:
21696405]
METHODS AND RESULTS:
The addition of Macrocarpal A, one of the main components of the Eucalyptus extract, to human keratinocytes in culture increased the level of ceramide and the mRNA expression of serine palmitoyltransferase, acid sphingomyelinase, neutral sphingomyelinase, glucosylceramide synthase and glucocerebrosidase in a dose-dependent manner.
CONCLUSIONS:
Our results indicate that the increased content of ceramides in the stratum corneum may underlie the therapeutic effect of the Eucalyptus extract. Our results also indicate the possibility that Macrocarpal A is the key component that stimulates the synthesis of ceramide in the stratum corneum.
Agr. Biol. Chem., 1990, 54(12):3221-6.
Macrocarpal A, a novel antibacterial compound from Eucalyptus macrocarpa.[Reference:
WebLink]
METHODS AND RESULTS:
A novel antibacterial compound, Macrocarpal A, was isolated from the leaves of , and its structure was determined on the basis of an X-ray crystal structure analysis.
CONCLUSIONS:
Macrocarpal A is composed of a phloroglucinol dialdehyde and diterpene, having a 3-membered ring, a 5-membered ring and a 7-membered ring.
Bioorg Med Chem Lett. 2007 Feb 15;17(4):1107-11.
Intestinal permeability of antivirus constituents from the fruits of Eucalyptus globulus Labill. in Caco-2 Cell Model.[Pubmed:
17118653]
The uptake and transepithelial transport of the three main constituents Macrocarpal A (M-A), macrocarpal B (M-B), and cypellocarpa C (Cy-C) from the fruits of Eucalyptus globulus Labill. were investigated.
METHODS AND RESULTS:
Monolayers of the human intestinal epithelial cancer cell line Caco-2 were incubated with Macrocarpal A, M-B, and Cy-C to model its intestinal absorption and transport, respectively. The determination of compounds was performed by HPLC. The apparent permeability coefficients (P(app)) for Macrocarpal A, M-B, and Cy-C in the apical-to-basolateral direction of a Caco-2 monolayer were (1.70+/-0.06)x10(-6), (1.99+/-0.10)x10(-6), and (6.08+/-0.41)x10(-6)cm/s, respectively. In the presence of iodoacetamide, the P(app) of Cy-C were both reducted in apical-to-basolateral and basolateral-to-apical directions. Macrocarpal A and M-B appear to accumulate in the epithelial cells.
CONCLUSIONS:
The intestinal absorption of Macrocarpal A, M-B, and Cy-C was passive diffusion as the dominating process and Cy-C was partly ATP-dependent.
J Nat Prod. 2013 Dec 27;76(12):2346-9.
Semisynthesis of macrocarpal C and analogues by selective dehydration of macrocarpal A or B.[Pubmed:
24261967]
METHODS AND RESULTS:
Macrocarpals A and C are structurally related compounds that have been extracted from different Eucalyptus species.
Although macrocarpal C is of biological interest, its isolation in pure form is difficult to achieve. We report herein an efficient method for the semisynthesis of macrocarpal C by selective exo-dehydration of another member of the macrocarpal family, Macrocarpal A.
CONCLUSIONS:
We also report the semisynthesis of three new macrocarpal structures derived from either Macrocarpal A or B.