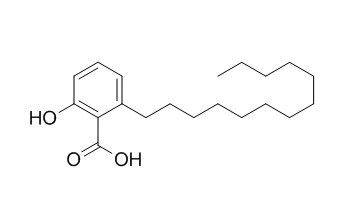
Ginkgolic acid C13:0
Ginkgolic acid C13:0 has a wide antimicrobial spectrum against E.coli and bacillus subtilis who are bacterias, and penicillium, penicillum purpurogenum, penicillium camemberti and aspergillus niger who are fungis, and the MIC of it against E.coli, bacillus subtilis and penicillium is 7.5, 15, 25 mg/mL seperately. It is a natural anticariogenic agent in that it exhibits antimicrobial activity against S. mutans and suppresses the specific virulence factors associated with its cariogenicity. Ginkgolic acid C13:0 exhibits the high α-glucosidase inhibitory activity; Ginkgolic acid C13:0 represents a new kind of molluscicide agent , it has a pronounced effect on snail mitochondria with gross ultrastructural changes.
Inquire / Order:
manager@chemfaces.com
Technical Inquiries:
service@chemfaces.com
Tel:
+86-27-84237783
Fax:
+86-27-84254680
Address:
1 Building, No. 83, CheCheng Rd., Wuhan Economic and Technological Development Zone, Wuhan, Hubei 430056, PRC
Providing storage is as stated on the product vial and the vial is kept tightly sealed, the product can be stored for up to
24 months(2-8C).
Wherever possible, you should prepare and use solutions on the same day. However, if you need to make up stock solutions in advance, we recommend that you store the solution as aliquots in tightly sealed vials at -20C. Generally, these will be useable for up to two weeks. Before use, and prior to opening the vial we recommend that you allow your product to equilibrate to room temperature for at least 1 hour.
Need more advice on solubility, usage and handling? Please email to: service@chemfaces.com
The packaging of the product may have turned upside down during transportation, resulting in the natural compounds adhering to the neck or cap of the vial. take the vial out of its packaging and gently shake to let the compounds fall to the bottom of the vial. for liquid products, centrifuge at 200-500 RPM to gather the liquid at the bottom of the vial. try to avoid loss or contamination during handling.
Evid Based Complement Alternat Med.2021, 2021:8847358.
Pharmaceutics.2022, 14(5):945.
Plant Cell Tiss Org2020, 1-16
Curr Pharm Des.2024, 30(1):71-80.
Br J Pharmacol.2016, 173(2):396-410
Nutrients.2021, 13(12):4364.
South African Journal of Botany2024, 168:209-220.
Applied Physics B2021, 127(92).
J. of The Korean Society of Food Culture2017, 144-149
Int J Mol Sci.2018, 19(9):E2528
Related and Featured Products
Journal of Chinese Institute of Food Science and Technology. 2015, 15(3):207-15.
Purification, identification and the antimicrobial activity of ginkgolic acids in ginkgo seeds.[Reference:
WebLink]
Ginkgo seeds were used as materials in this experiment, Ginkgolic acids in ginkgo seeds were extracted by ethanol, and the ethanol extract were further extracted with petroleum ether.
METHODS AND RESULTS:
The purification process of the ginkgolic acids were studied, and the compositions and contents were analyzed and detected by the methods of combination of HPLC and LC-MS. And two bacterias and four fungis were used for tested strains, the antimicrobial activity of ginkgolic acids were tested and the minimal inhibitory concentration (MIC) were determined separately. The results show that taking 89:1:11 system of petroleum ether, ethyl ether, and methanol as eluents, at 1.2 mL/min velocity, the effect of the silica gel column chromatography purification is the better. HPLC and LC -MS analysis showed that ginkgolic acids in ginkgo seeds consists chiefly of Ginkgolic acid C13:0, C15:1, C17:2, C15:0, C17:1. The content of ginkgolic acids in skimmed ginkgo powder is 0.11 g/kg by the C13:0, C15:1, C17:1 and the content of Ginkgolic acid C13:0, C15:1, C17:1 is 0.013, 0.042, 0.055 g/kg separately.
CONCLUSIONS:
The antimicrobial tests showed that ginkgolic acids had a wide antimicrobial spectrum against E.coli and bacillus subtilis who are bacterias, and penicillium, penicillum purpurogenum, penicillium camemberti and aspergillus niger who are fungis. And the MIC of the ginkgolic acids against E.coli, bacillus subtilis and penicillium is 7.5, 15, 25 mg/mL seperately.
Aquaculture, 2009, 297(1-4):38-43.
In vivo assessment of anthelmintic efficacy of ginkgolic acids (C13:0, C15:1) on removal of Pseudodactylogyrus in European eel[Reference:
WebLink]
Pseudodactylogyrus is a significant monogenean parasite of the gills of aquacultured European eels, and can cause severe gill pathology.
In this study, effects of the crude extracts, fractions and compounds of exopleura of Ginkgo biloba against Pseudodactylogyrus were investigated under in vivo conditions by bio-assay guided isolation method.
METHODS AND RESULTS:
Four solvents (petroleum ether, ethyl acetate, n-butanol and water) were applied for the extraction of exopleura of G. biloba. Among them, only the petroleum ether extract showed strong activity and therefore, subjected to further separation and purification using various chromatographic techniques. Two compounds showing potent activity were identified by comparing spectral data (IR, NMR, and EI-MS) with literature values to be Ginkgolic acid C13:0 and C15:1. They were found to be 100% effective at the concentration of 2.5 mg l- 1 and 6.0 mg l- 1, with ED50 values of 0.72 mg l- 1 and 2.88 mg l- 1, respectively. In the 5-days safety test, Ginkgolic acid C13:0 and C15:1 were shown to be safe for healthy juvenile eels when the concentration were up to 10.0 and 18.0 mg l- 1, respectively.
CONCLUSIONS:
The two compounds exhibited potential results and can be explored as plant-derived antiparasitic for the control of Pseudodactylogyrus.
Pak J Biol Sci. 2014 Nov;17(11):1170-8.
Potent α-glucosidase inhibitors isolated from Ginkgo biloba leaves.[Pubmed:
26027162]
In vitro α-glucosidase inhibitory activity of Ginkgo biloba leaves was investigated.
METHODS AND RESULTS:
The inhibitory activity of methanol extracts from yellow and green leaves was 13.8 and 40.1 μg mL(-1), respectively. Each methanol extract was separated into its respective fraction by solvent-solvent extraction with n-hexane, chloroform, ethyl acetate and n-butanol. The n-hexane fractions (in both methanol extracts from green and yellow leaves) exhibited high α-glucosidase inhibitory activity with IC50 values of 13.6 and 13.4 μg mL(-1), respectively. Further fractionation of the n-hexane fractions by silica gel column chromatography gave the most active fraction which was identified as Ginkgolic acid C13:0 and a mixture (C13:0, C15:0, C15: 1, C17:1 and C17:2). Ginkgolic acid C13:0 exhibited the highest α-glucosidase inhibitory activity.
CONCLUSIONS:
This is the first study to successfully isolate ginkgolic acids as α-glucosidase inhibitors.
Pestic. Biochem. Phys., 2012, 103(2):115-20.
Effects of the molluscicidal agent GA-C13:0, a natural occurring ginkgolic acid, on snail mitochondria.[Reference:
WebLink]
Ginkgolic acids (GAs) from the leaves and sarcotesta of Ginkgo biloba L. represent a new kind of molluscicide agent. To date, the mechanism(s) for the observed molluscicidal activity remains largely unknown. Since Ginkgolic acid C13:0(GA-C13:0) has effectively inhibited snail mobility, we examined the effects of the compound on mitochondrial function and gene expression as compared to niclosamide.
METHODS AND RESULTS:
Snail mitochondrial damage induced by GAs was tested using transmission electron microscopy (TEM) and gene-expression profiling of five mitochondrial enzymes using real-time PCR. GA-C13:0 was found to have a pronounced effect on snail mitochondria with gross ultrastructural changes. In addition, GA-C13:0 was also found to inhibit the gene expression of four mitochondrial enzymes including cytochrome c oxidase, adenosine triphosphate (ATP) synthase, cytochrome b and dihydronicotinamide adenine dinucleotide (NADH) dehydrogenase. In contrast, niclosamide did not show such effects on mitochondrial function and gene expression, suggesting that the molluscicidal activity of GA-C13:0 and niclosamide differed.
CONCLUSIONS:
Our results imply that snail mitochondria are a potential target for the molluscicidal activity of ginkgolic acids.