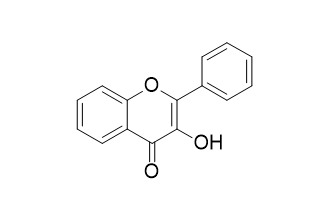
Flavonol
Flavonol has antioxidant activity.
Inquire / Order:
manager@chemfaces.com
Technical Inquiries:
service@chemfaces.com
Tel:
+86-27-84237783
Fax:
+86-27-84254680
Address:
1 Building, No. 83, CheCheng Rd., Wuhan Economic and Technological Development Zone, Wuhan, Hubei 430056, PRC
Providing storage is as stated on the product vial and the vial is kept tightly sealed, the product can be stored for up to
24 months(2-8C).
Wherever possible, you should prepare and use solutions on the same day. However, if you need to make up stock solutions in advance, we recommend that you store the solution as aliquots in tightly sealed vials at -20C. Generally, these will be useable for up to two weeks. Before use, and prior to opening the vial we recommend that you allow your product to equilibrate to room temperature for at least 1 hour.
Need more advice on solubility, usage and handling? Please email to: service@chemfaces.com
The packaging of the product may have turned upside down during transportation, resulting in the natural compounds adhering to the neck or cap of the vial. take the vial out of its packaging and gently shake to let the compounds fall to the bottom of the vial. for liquid products, centrifuge at 200-500 RPM to gather the liquid at the bottom of the vial. try to avoid loss or contamination during handling.
Kaohsiung J Med Sci.2024, 40(3):280-290.
J Mater Chem B.2019, 7(39):5896-5919
Molecules.2017, 22(6)
J Ethnopharmacol.2019, 236:31-41
J Sci Food Agric.2022, 102(4):1628-1639
Microbiol. Biotechnol. Lett.2022, 50(2): 193-201.
PLoS One.2018, 13(11):e0208055
Nat Chem Biol.2018, 14(8):760-763
Drug Chem Toxicol.2020, 1-12.
Mol Neurobiol.2021, 58(8):3665-3676.
Related and Featured Products
J Agric Food Chem, 2010, 46(10):4107-4112.
Antioxidant activity of berry phenolics on human low-density lipoprotein and liposome oxidation.[Reference:
WebLink]
METHODS AND RESULTS:
The antioxidant activity of phenolic compounds present in berries was investigated by two copper-catalyzed in vitro oxidation assays: human low-density lipoproteins (LDL) and lecithin liposomes. The amount of total phenolics varied between 617 and 4350 mg/kg in fresh berries, as gallic acid equivalents (GAE). In LDL at 10 μM GAE, berry extracts inhibited hexanal formation in the order: blackberries > red raspberries > sweet cherries > blueberries > strawberries. In lecithin liposomes, the extracts inhibited hexanal formation in the order: sweet cherries > blueberries > red raspberries > blackberries > strawberries. Red raspberries were more efficient than blueberries in inhibiting hydroperoxide formation in lecithin liposomes. HPLC analyses showed high anthocyanin content in blackberries, hydroxycinnamic acid in blueberries and sweet cherries, Flavonol in blueberries, and flavan-3-ol in red raspberries. The antioxidant activity for LDL was associated directly with anthocyanins and indirectly with Flavonols, and for liposome it correlated with the hydroxycinnamate content.
CONCLUSIONS:
Berries thus contribute a significant source of phenolic antioxidants that may have potential health effects.