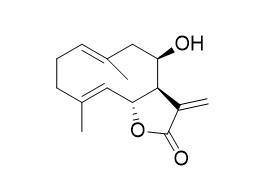
Eupatolide
Eupatolide has anti-inflammatory activity, it inhibits lipopolysaccharide-induced COX-2 and iNOS expression in RAW264.7 cells by inducing proteasomal degradation of TRAF6. It can suppress PDGF-induced proliferation and migration of VSMC through HO-1 induction via ROS-Nrf2 pathway and may be a potential HO-1 inducer for preventing or treating vascular diseases. Eupatolide exhibits potent cytotoxicity against HL-60, SMMC-7721, A-549, MCF-7, and SW-480 cancer cell lines, with IC50 values ranging from 1.57 to 22.58 uM; it sensitizes breast cancer cells to TRAIL through down-regulation of c-FLIP expression, it is a valuable compound to overcome TRAIL resistance in breast cancer cells.
Inquire / Order:
manager@chemfaces.com
Technical Inquiries:
service@chemfaces.com
Tel:
+86-27-84237783
Fax:
+86-27-84254680
Address:
1 Building, No. 83, CheCheng Rd., Wuhan Economic and Technological Development Zone, Wuhan, Hubei 430056, PRC
Providing storage is as stated on the product vial and the vial is kept tightly sealed, the product can be stored for up to
24 months(2-8C).
Wherever possible, you should prepare and use solutions on the same day. However, if you need to make up stock solutions in advance, we recommend that you store the solution as aliquots in tightly sealed vials at -20C. Generally, these will be useable for up to two weeks. Before use, and prior to opening the vial we recommend that you allow your product to equilibrate to room temperature for at least 1 hour.
Need more advice on solubility, usage and handling? Please email to: service@chemfaces.com
The packaging of the product may have turned upside down during transportation, resulting in the natural compounds adhering to the neck or cap of the vial. take the vial out of its packaging and gently shake to let the compounds fall to the bottom of the vial. for liquid products, centrifuge at 200-500 RPM to gather the liquid at the bottom of the vial. try to avoid loss or contamination during handling.
Pharmaceuticals (Basel).2021, 14(8):742.
Hindawi J of Food Biochemistry2023, P17:8883860
J Agric Food Chem.2021, 69(46):14037-14047.
Hum. Ecol. Res.2025, 63(2):165-174
Egyptian Pharmaceutical Journal2024, epj_205_23.
Front Pharmacol.2020, 11:683.
J Liq Chromatogr R T2025, 2505536.
Antioxidants (Basel).2020, 9(2): E119
Brain Res Bull.2024, 218:111103.
Evid Based Complement Alternat Med.2021, 2021:8707280.
Related and Featured Products
Phytochemistry. 2016 Sep;129:68-76.
Bioactive sesquiterpenoids from the flowers of Inula japonica.[Pubmed:
27452450]
METHODS AND RESULTS:
Phytochemical investigation of the flowers of Inula japonica led to isolation of nine sesquiterpenoids, inujaponins A-I, as well as eighteen known ones. These sesquiterpenoids belong to six skeletal-types, including eudesmane, 1,10-seco-eudesmane, germacrane, guaiane, 4,5-seco-guaiane, and pseudoguaiane sesquiterpenoids. Their structures were established by extensive spectroscopic analysis. The absolute configurations of inujaponin A, Eupatolide, and deacetylovatifolin were determined by Cu-Kα X-ray crystallographic analysis.
CONCLUSIONS:
Most of the isolated compounds exhibited potent cytotoxicity against HL-60, SMMC-7721, A-549, MCF-7, and SW-480 cancer cell lines, with IC50 values ranging from 1.57 to 22.58 μM. Some selected compounds also possessed significant inhibitory activity against LPS-induced NO production in RAW264.7 macrophages with IC50 values ranging from 1.42 to 8.99 μM.
Eur J Pharmacol. 2010 Jun 25;636(1-3):173-80.
Eupatolide inhibits lipopolysaccharide-induced COX-2 and iNOS expression in RAW264.7 cells by inducing proteasomal degradation of TRAF6.[Pubmed:
20353767 ]
Inula britannica is a traditional medicinal plant used to treat bronchitis, digestive disorders, and inflammation in Eastern Asia.
METHODS AND RESULTS:
Here, we identified Eupatolide, a sesquiterpene lactone from I. britannica, as an inhibitor of cyclooxygenase-2 (COX-2) and inducible nitric oxide synthase (iNOS) expression. Eupatolide inhibited the production of nitric oxide (NO) and prostaglandin E(2) (PGE(2)) as well as iNOS and COX-2 protein expression in lipopolysaccharide (LPS)-stimulated RAW264.7 cells. Eupatolide dose-dependently decreased the mRNA levels and the promoter activities of COX-2 and iNOS in LPS-stimulated RAW264.7 cells. Moreover, Eupatolide significantly suppressed the LPS-induced expression of nuclear factor-kappa B (NF-kappaB) and activator protein-1 (AP-1) reporter genes. Pretreatment of Eupatolide inhibited LPS-induced phosphorylation and degradation of I kappaB alpha, and phosphorylation of RelA/p65 on Ser-536 as well as the activation of mitogen-activated protein kinases (MAPKs) and Akt in LPS-stimulated RAW264.7 cells. Eupatolide induced proteasomal degradation of tumor necrosis factor receptor-associated factor-6 (TRAF6), and subsequently inhibited LPS-induced TRAF6 polyubiquitination.
CONCLUSIONS:
These results suggest that Eupatolide blocks LPS-induced COX-2 and iNOS expression at the transcriptional level through inhibiting the signaling pathways such as NF-kappaB and MAPKs via proteasomal degradation of TRAF6. Taken together, Eupatolide may be a novel anti-inflammatory agent that induces proteasomal degradation of TRAF6, and a valuable compound for modulating inflammatory conditions.
Phytother Res. 2013 Nov;27(11):1700-7.
Eupatolide inhibits PDGF-induced proliferation and migration of aortic smooth muscle cells through ROS-dependent heme oxygenase-1 induction.[Pubmed:
23297002]
The abnormal proliferation and migration of vascular smooth muscle cell (VSMC) contributes importantly to the pathogenesis of atherosclerosis and restenosis.
METHODS AND RESULTS:
Here, we investigated the effects of Eupatolide (EuTL), a sesquiterpene lactone isolated from the medicinal plant Inula britannica, on platelet-derived growth factor (PDGF)-induced proliferation and migration of primary rat aortic smooth muscle cells (RASMCs), as well as its underlying mechanisms. EuTL remarkably inhibited PDGF-induced proliferation and migration of RASMCs. Treatment of RASMCs with EuTL induced both protein and mRNA expression of heme oxygenase-1 (HO-1). SB203580 (a p38 inhibitor), SP600125 (a JNK inhibitor), U0126 (a MEK inhibitor) and LY294002 (a PI3K inhibitor) did not suppress EuTL-induced HO-1 expression; however, N-acetylcysteine (NAC, an antioxidant) blocked EuTL-induced HO-1 expression. Moreover, treatment of RASMCs with EuTL increased reactive oxygen species (ROS) accumulation and nuclear translocation of nuclear factor-E2-related factor 2 (Nrf2); however, this translocation was also inhibited by NAC. NAC or inhibition of HO-1 significantly attenuated the inhibitory effects of EuTL on PDGF-induced proliferation and migration of RASMCs.
CONCLUSIONS:
Taken together, these findings suggest that EuTL could suppress PDGF-induced proliferation and migration of VSMCs through HO-1 induction via ROS-Nrf2 pathway and may be a potential HO-1 inducer for preventing or treating vascular diseases.
Planta Med. 2006 Jan;72(1):40-5.
New sesquiterpene dimers from Inula britannica inhibit NF-kappaB activation and NO and TNF-alpha production in LPS-stimulated RAW264.7 cells.[Pubmed:
16450294 ]
METHODS AND RESULTS:
A bioassay-guided isolation of an ethyl acetate-soluble extract of the aerial parts of Inula britannica var. chinensis (Rupr.) Regel, using an in vitro NF-kappaB reporter gene assay, led to the isolation of four new sesquiterpene dimers bearing a norbornene moiety, inulanolides A-D, and three known sesquiterpenes, 1,6alpha-dihydroxyeriolanolide, 1-acetoxy-6alpha-hydroxyeriolanolide, and Eupatolide. The structures of the new compounds were elucidated by spectroscopic methods.
CONCLUSIONS:
Among these compounds, inulanolides B and D and Eupatolide, exhibited potent inhibitory activity on the LPS-induced NF-kappaB activation with IC50 values of 0.49 microM, 0.48 microM, and 1.54 microM, respectively.
Consistent with their inhibitory effect on NF-kappaB activation, compounds and also strongly inhibited the production of NO and TNF-alpha in the LPS-stimulated RAW264.7 cells with IC50 values in the range of 2 microM.