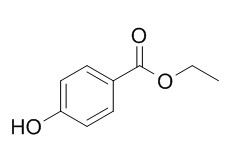
Ethylparaben
Ethylparaben is the ethyl ester of p-hydroxybenzoic acid, used as an antifungal preservative and food additive. It is a standardized chemical allergen, has a certain reproductive toxicity to F0 male Drosophila.The physiologic effect of ethylparaben is by means of Increased Histamine Release, and Cell-mediated Immunity.
Inquire / Order:
manager@chemfaces.com
Technical Inquiries:
service@chemfaces.com
Tel:
+86-27-84237783
Fax:
+86-27-84254680
Address:
1 Building, No. 83, CheCheng Rd., Wuhan Economic and Technological Development Zone, Wuhan, Hubei 430056, PRC
Providing storage is as stated on the product vial and the vial is kept tightly sealed, the product can be stored for up to
24 months(2-8C).
Wherever possible, you should prepare and use solutions on the same day. However, if you need to make up stock solutions in advance, we recommend that you store the solution as aliquots in tightly sealed vials at -20C. Generally, these will be useable for up to two weeks. Before use, and prior to opening the vial we recommend that you allow your product to equilibrate to room temperature for at least 1 hour.
Need more advice on solubility, usage and handling? Please email to: service@chemfaces.com
The packaging of the product may have turned upside down during transportation, resulting in the natural compounds adhering to the neck or cap of the vial. take the vial out of its packaging and gently shake to let the compounds fall to the bottom of the vial. for liquid products, centrifuge at 200-500 RPM to gather the liquid at the bottom of the vial. try to avoid loss or contamination during handling.
Front. Pharmacol.2022, 901563.
Food Analytical Methods2020, 1-10
Evid Based Complement Alternat Med.2021, 2021:5319584.
J. Food Composition and Anal.2022, V 109:104482.
J Pharm Biomed Anal.2016, 129:50-59
J of Apicultural Research2020, 10.1080
Antimicrob Agents Chemother.2024, e0031424.
Biomed Pharmacother.2022, 156:113929.
Cell Physiol Biochem.2017, 43(4):1425-1435
Biomolecules.2024, 14(4):451.
Related and Featured Products
Microbiol Res. 2015 Mar;172:48-56.
Identification of ethylparaben as the antimicrobial substance produced by Brevibacillus brevis FJAT-0809-GLX.[Pubmed:
25542595]
METHODS AND RESULTS:
In this study, crude antimicrobial extract from the culture supernatant of Brevibacillus brevis FJAT-0809-GLX was extracted, and its antimicrobial activity was investigated with the agar diffusion method. The results showed that the antimicrobial activity of the culture supernatant of B. brevis FJAT-0809-GLX increased with the extension of the incubation time of B. brevis FJAT-0809-GLX. The antimicrobial spectrum assays showed that this crude antimicrobial extract from culture supernatant of B. brevis FJAT-0809-GLX could inhibit the growth of both bacteria and fungi. A heat stability test was performed, and different temperatures (30°C, 50°C and 70°C) did not affect the antibiotic activity of this crude antimicrobial extract. The crude antimicrobial extract was also tolerable to changes in pH levels. Its antibiotic activity against Escherichia coli was stable at pH 1 to pH 11, with zone sizes ranging from 18.46mm to 22.19mm. Almost all of the crude extracts extracted using different solvents showed variable degrees of inhibition zones against E. coli, with zone sizes ranging from 17.29mm to 19.62mm, except petroleum ether and butanol extracts, which were found to be completely inactive. Purification of the antimicrobial components was carried out using a column chromatographic technique with column chromatography grade silica gel and analyzed by an Agilent 7890A Network GC system. The separated compound was identified as Ethylparaben, with a retention time of 21.980min and a relative amount of 95.50%.
CONCLUSIONS:
The antimicrobial activity of Ethylparaben on different types of bacteria and fungi was investigated, and Ethylparaben was shown to inhibit different types of microbes to different extents. To the best of our knowledge, this is the first report demonstrating that the bacterium B. brevis could produce Ethylparaben.
J Insect Physiol. 2014 Dec;71:1-7.
Ethylparaben affects lifespan, fecundity, and the expression levels of ERR, EcR and YPR in Drosophila melanogaster.[Pubmed:
25265034]
Parabens, which mainly include mEthylparaben (MP), Ethylparaben (EP), propylparaben (PP), and butylparaben (BP), are widely used as cosmetic and food preservatives.
Although these chemicals, when used as preservatives, are thought to be safe for humans, many studies have demonstrated that they have estrogenic effects, and can affect the normal development and functions of the reproductive systems in a number of animal species.
METHODS AND RESULTS:
By treating fruit flies (Drosophila melanogaster) with EP, here we show that lower concentration of EP (0.02%) enhanced fertility while higher concentration of EP (0.10% and 0.20%) shortened the lifespan and reduced the fecundity of fruit flies. When we analyzed the expression levels of the estrogen-related receptor gene (ERR), ecdysone receptor gene (EcR) and Yolk protein receptor gene (YPR) from control and EP-treated fruit flies by using quantitative real-time PCR, we found that the expression levels of all three genes were significantly changed by EP treatment, and that female fruit flies are more sensitive to EP than males.
CONCLUSIONS:
Our data suggests that the estrogenic and the toxic effects of EP to fruit flies may have a molecular basis through the hormonal effect of EP.
Wei Sheng Yan Jiu. 2014 Mar;43(2):265-70.
[Reproductive toxicity of ethylparaben on male Drosophila melanogaster].[Pubmed:
24868981]
To investigate the reproductive toxicity of different concentration of Ethylparaben (EP) on male Drosophila.
METHODS AND RESULTS:
New eclosion flies within 8h in the basal medium were collected and male Drosophila among them were put into control group and EP treating groups with different concentration (0.03%, 0.07% and 0.10%) by random selection. Female Drosophila was all put into control group. After cultured for 5 days by one pair in one tube and 10 times of repetition for each group, the egg laying amount and maximum egg laying amount of 10d parental generation (F0) and first filial generation (F1), the emergence rate and emergence amount of F1 and second finial generation (F2), the duration time of eggs-arvae, larvae-pupa, and pupa-adult flies, and the total duration time of emergence were counted.
The egg laying amount, emergence rate and emergence amount of EP treated parental Drosophila were significantly lower than those of the control group (P < 0.01). The total duration time of emergence of F1 prolongs with the increase of EP concentration. The egg laying amount of F1 and emergence rate of F2 in high EP concentration group had remarkable different compared to those of control group (P < 0.01). And the total duration time of F2 had also shortened significantly compared to that of control group (P < 0.05), while there was no remarkable difference in 0.03% and 0.07% concentration group.
CONCLUSIONS:
EP has a certain reproductive toxicity to F0 male Drosophila and EP of high concentration can impact sustainable to offspring which has some facilitation effect on F1 Drosophila.
Indian J Pharm Sci. 2010 Jul;72(4):421-5.
A New Validated HPLC Method for the Simultaneous Determination of 2-phenoxyethanol, Methylparaben, Ethylparaben and Propylparaben in a Pharmaceutical Gel.[Pubmed:
21218050]
METHODS AND RESULTS:
A novel reversed-phase HPLC method has been developed and validated for the simultaneous determination of 2-phenoxyethanol, mEthylparaben, Ethylparaben and propylparaben preservatives. The method uses a Lichrosorb C8 (150×4.6 mm, 5 μm) column and isocratic elution. The mobile phase consisted of a mixture of acetonitrile, tetrahydrofuran and water (21:13:66, v/v/v), pumped at a flow rate of 1 ml/min. The UV detection was set at 258 nm. The method was validated with respect to accuracy, precision (repeatability and intermediate precision), specificity, linearity and range. All the parameters examined met the current recommendations for bioanalytical method validation.
CONCLUSIONS:
The developed method was successfully applied to the determination of commercially available pharmaceutical gel products for these preservatives. The procedure describes here is simple, selective and reliable for routine quality control analysis and stability tests.