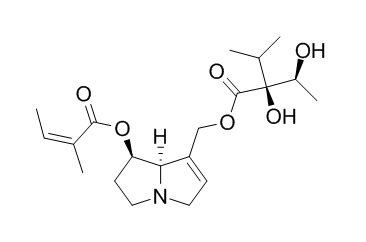
Echiumine
Reference standards.
Inquire / Order:
manager@chemfaces.com
Technical Inquiries:
service@chemfaces.com
Tel:
+86-27-84237783
Fax:
+86-27-84254680
Address:
1 Building, No. 83, CheCheng Rd., Wuhan Economic and Technological Development Zone, Wuhan, Hubei 430056, PRC
Providing storage is as stated on the product vial and the vial is kept tightly sealed, the product can be stored for up to
24 months(2-8C).
Wherever possible, you should prepare and use solutions on the same day. However, if you need to make up stock solutions in advance, we recommend that you store the solution as aliquots in tightly sealed vials at -20C. Generally, these will be useable for up to two weeks. Before use, and prior to opening the vial we recommend that you allow your product to equilibrate to room temperature for at least 1 hour.
Need more advice on solubility, usage and handling? Please email to: service@chemfaces.com
The packaging of the product may have turned upside down during transportation, resulting in the natural compounds adhering to the neck or cap of the vial. take the vial out of its packaging and gently shake to let the compounds fall to the bottom of the vial. for liquid products, centrifuge at 200-500 RPM to gather the liquid at the bottom of the vial. try to avoid loss or contamination during handling.
J Physiol Biochem.2024, 80(2):421-437.
Plants (Basel).2023, 12(11):2107.
Front Microbiol.2022, 12:833233.
Food Chem. 2020, 320:126530
Foods.2020, 9(10):1348.
J Integr Plant Biol.2023, 13564.
Bull.Natl.Mus.Nat.Sci.,Ser.B.2024, 50(2):79ĘC86
Anal Chim Acta.2018, 1039:162-171
Planta Med.2019, 85(4):347-355
American Association for Anatomy2020, doi: 10.1002.
Related and Featured Products
Phytochem Anal. 2011 Nov-Dec;22(6):532-40.
Detection of high levels of pyrrolizidine-N-oxides in the endangered plant Cryptantha crassipes (Terlingua Creek cat's-eye) using HPLC-ESI-MS.[Pubmed:
21433162]
A previous investigation of pyrrolizidine alkaloids produced by nine species of Cryptantha identified at least two chemotypes within the genus. Other research has postulated that pyrrolizidine-N-oxide concentrations increase as the growing conditions become harsher, particularly with respect to water availability. Cryptantha crassipes is an endangered plant with a very limited distribution range within a dry, harsh Texan ecosystem.
To determine the pyrrolizidine alkaloid (and their N-oxides) profile and concentrations in Cryptantha crassipes.
METHODS AND RESULTS:
Methanolic extracts of Cryptantha crassipes were partitioned into dilute sulphuric acid and the alkaloids concentrated using strong cation exchange, solid-phase extraction columns. Extracts were analysed using reversed-phase high-pressure liquid chromatography coupled to electrospray ionisation ion trap mass spectrometry.
The N-oxides of lycopsamine and intermedine were the major pyrrolizidine alkaloids detected in Cryptantha crassipes. Smaller to trace amounts of other pyrrolizidine alkaloids observed were: the 7- and 3'-acetylated derivatives and the 1,2-dihydro analogs of lycopsamine-N-oxide and/or intermedine-N-oxide; a pair of unidentified N-oxides, isobaric with lycopsamine-N-oxide; and the N-oxides of leptanthine, echimiplatine, amabiline, Echiumine and dihydroEchiumine. Only trace amounts, if any, of the parent free base pyrrolizidine alkaloids were detected. The concentration of pyrrolizidine alkaloids was estimated to be 3-5% of the dry weight of milled leaves, or 10-50 times the levels previously reported for similar chemotypes.
CONCLUSIONS:
The high levels of the N-oxides of lycopsamine and intermedine establish the genus chemotype of the endangered Cryptantha crassipes and support earlier data linking high levels of N-oxides to dry, harsh growing conditions.