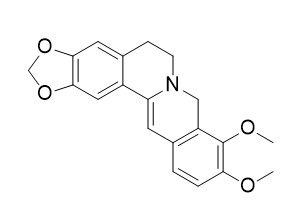
Dihydroberberine
Dihydroberberine has anti-tumor activity. It also improves in vivo efficacy in terms of counteracting increased adiposity, tissue triglyceride accumulation, and insulin resistance in high-fat-fed rodents, thus is potential therapeutic reagents for type 2 diabetes treatment.
Inquire / Order:
manager@chemfaces.com
Technical Inquiries:
service@chemfaces.com
Tel:
+86-27-84237783
Fax:
+86-27-84254680
Address:
1 Building, No. 83, CheCheng Rd., Wuhan Economic and Technological Development Zone, Wuhan, Hubei 430056, PRC
Providing storage is as stated on the product vial and the vial is kept tightly sealed, the product can be stored for up to
24 months(2-8C).
Wherever possible, you should prepare and use solutions on the same day. However, if you need to make up stock solutions in advance, we recommend that you store the solution as aliquots in tightly sealed vials at -20C. Generally, these will be useable for up to two weeks. Before use, and prior to opening the vial we recommend that you allow your product to equilibrate to room temperature for at least 1 hour.
Need more advice on solubility, usage and handling? Please email to: service@chemfaces.com
The packaging of the product may have turned upside down during transportation, resulting in the natural compounds adhering to the neck or cap of the vial. take the vial out of its packaging and gently shake to let the compounds fall to the bottom of the vial. for liquid products, centrifuge at 200-500 RPM to gather the liquid at the bottom of the vial. try to avoid loss or contamination during handling.
J Ginseng Res.2023, 47(4):572-582.
Journal of Molecular Liquids2022, 364:120062.
FASEB J.2019, 33(8):9685-9694
J Agric Food Chem.2022, 70(51):16176-16187.
J Basic Clin Physiol Pharmacol.2016, 27(1):1-8
J Microbiol Biotechnol.2022, 32(2):141-148.
Ind. J. Pharm. Edu. Res.2023; 57(3):1132-1139.
Nutr Res Pract.2020, 14(5):478-489.
Polytechnic University of Catalonia2017, 105826
Br J Pharmacol.2020, 10.1111
Related and Featured Products
Arch Pharm Res. 1997 Oct;20(5):476-9.
Studies on the synthesis andin vitro anti-tumor activity of dihydroberberine derivatives.[Pubmed:
18982493]
METHODS AND RESULTS:
Three types of Dihydroberberine derivatives such as spirobenzylisoquinoline, benzindenoazepine and cyclopropanated quinolizine species were synthesized from Dihydroberberine for the investigation on their anti-tumor activity.
CONCLUSIONS:
Among them, cyclopropanated quinolizine species were more effective than spirobenzylisoquinoline and benzindenoazepine against P-388 and L-1210 leukemia cell.
Diabetes. 2008 May;57(5):1414-8.
Berberine and its more biologically available derivative, dihydroberberine, inhibit mitochondrial respiratory complex I: a mechanism for the action of berberine to activate AMP-activated protein kinase and improve insulin action.[Pubmed:
18285556]
Berberine (BBR) activates AMP-activated protein kinase (AMPK) and improves insulin sensitivity in rodent models of insulin resistance. We investigated the mechanism of activation of AMPK by BBR and explored whether derivatization of BBR could improve its in vivo efficacy.
METHODS AND RESULTS:
AMPK phosphorylation was examined in L6 myotubes and LKB1(-/-) cells, with or without the Ca(2+)/calmodulin-dependent protein kinase kinase (CAMKK) inhibitor STO-609. Oxygen consumption was measured in L6 myotubes and isolated muscle mitochondria. The effect of a BBR derivative, Dihydroberberine (dhBBR), on adiposity and glucose metabolism was examined in rodents fed a high-fat diet. We have made the following novel observations: 1) BBR dose-dependently inhibited respiration in L6 myotubes and muscle mitochondria, through a specific effect on respiratory complex I, similar to that observed with metformin and rosiglitazone; 2) activation of AMPK by BBR did not rely on the activity of either LKB1 or CAMKKbeta, consistent with major regulation at the level of the AMPK phosphatase; and 3) a novel BBR derivative, dhBBR, was identified that displayed improved in vivo efficacy in terms of counteracting increased adiposity, tissue triglyceride accumulation, and insulin resistance in high-fat-fed rodents. This effect is likely due to enhanced oral bioavailability.
CONCLUSIONS:
Complex I of the respiratory chain represents a major target for compounds that improve whole-body insulin sensitivity through increased AMPK activity. The identification of a novel derivative of BBR with improved in vivo efficacy highlights the potential importance of BBR as a novel therapy for the treatment of type 2 diabetes.
Bioorg Med Chem. 2010 Aug 15;18(16):5915-24.
8,8-Dimethyldihydroberberine with improved bioavailability and oral efficacy on obese and diabetic mouse models.[Pubmed:
20663675]
The clinical use of the natural alkaloid berberine (BBR) as an antidiabetic reagent is limited by its poor bioavailability. Our previous work demonstrated that Dihydroberberine (dhBBR) has enhanced bioavailability and in vivo efficacy compared with berberine.
METHODS AND RESULTS:
Here we synthesized the 8,8-dimethylDihydroberberine (Di-Me) with improved stability, and bioavailability over dhBBR. Similar to BBR and dhBBR, Di-Me inhibited mitochondria respiration, increased AMP:ATP ratio, activated AMPK and stimulated glucose uptake in L6 myotubes. In diet-induced obese (DIO) mice, Di-Me counteracted the increased adiposity, tissue triglyceride accumulation and insulin resistance, and improved glucose tolerance at a dosage of 15mg/kg. Administered to db/db mice with a dosage of 50mg/kg, Di-Me effectively reduced random fed and fasting blood glucose, improved glucose tolerance, alleviated insulin resistance and reduced plasma triglycerides, with better efficacy than dhBBR at the same dosage.
CONCLUSIONS:
Our work highlights the importance of Dihydroberberine analogs as potential therapeutic reagents for type 2 diabetes treatment.