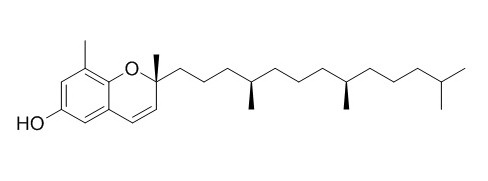
Dehydro-Delta-tocopherol
Dehydro-δ-tocopherol shows antioxidant capacities.
Inquire / Order:
manager@chemfaces.com
Technical Inquiries:
service@chemfaces.com
Tel:
+86-27-84237783
Fax:
+86-27-84254680
Address:
1 Building, No. 83, CheCheng Rd., Wuhan Economic and Technological Development Zone, Wuhan, Hubei 430056, PRC
Providing storage is as stated on the product vial and the vial is kept tightly sealed, the product can be stored for up to
24 months(2-8C).
Wherever possible, you should prepare and use solutions on the same day. However, if you need to make up stock solutions in advance, we recommend that you store the solution as aliquots in tightly sealed vials at -20C. Generally, these will be useable for up to two weeks. Before use, and prior to opening the vial we recommend that you allow your product to equilibrate to room temperature for at least 1 hour.
Need more advice on solubility, usage and handling? Please email to: service@chemfaces.com
The packaging of the product may have turned upside down during transportation, resulting in the natural compounds adhering to the neck or cap of the vial. take the vial out of its packaging and gently shake to let the compounds fall to the bottom of the vial. for liquid products, centrifuge at 200-500 RPM to gather the liquid at the bottom of the vial. try to avoid loss or contamination during handling.
J Agric Food Chem.2024, 72(15):8784-8797.
Vojnosanit Pregl2016, 75(00):391-391
Microbiol. Biotechnol. Lett.2022, 50(2): 193-201.
Heliyon.2022, 8(12):e12031.
J Pain Res.2022, 15:3469-3478.
Kangwon National University2022, 37(1):29-37
Pharmacogn Mag.2015, 11(43):562-6
Oxid Med Cell Longev.2022, 2022:5888636.
Pharmacol Rep.2019, 71(2):289-298
Comp. & Mathematical Methods in Med.2022, 5475559.
Related and Featured Products
Phytochemistry. 2004 Oct;65(19):2719-29.
Antioxidant dehydrotocopherols as a new chemical character of Stemona species.[Pubmed:
15464160]
METHODS AND RESULTS:
From the roots of various Stemona species four new dehydrotocopherols (chromenols) were isolated and their structures and stereochemistry elucidated by spectroscopic methods. The double bond between C-3 and C-4 proved to be a typical chemical character of the genus found in most of the species. Various C-methylations of the aromatic ring reflect differences in methyltransferase activities and agreed with the current species delimitations showing an exclusive accumulation of Dehydro-δ-tocopherol for the Stemona tuberosa group, whereas different provenances of Stemona curtisii were characterized by dehydro-gamma-tocopherol accompanied by small amounts of dehydro-alpha-tocopherol. From Stemona collinsae all four tocopherols were isolated with a clear preponderance of Dehydro-δ-tocopherol accompanied by smaller amounts of the rare dehydro-beta-tocopherol. Stemona burkillii and a group of unidentified species showed a weak accumulation trend towards dehydro-alpha-tocopherol, whereas Stemona cochinchinensis and especially Stemona kerrii clearly differed by a preponderance of chromanol derivatives. In Stemona cf. pierrei no tocopherols could be detected at all.
CONCLUSIONS:
Based on TLC tests and microplate assays with the free radical 2,2-diphenyl-1-picrylhydrazyl (DPPH*) the antioxidant capacities of all chromenol derivatives were comparable with that of alpha-tocopherol showing no significant differences among each other, except for a more rapid kinetic behaviour of the 5,7,8-methylated dehydro-alpha-tocopherol.