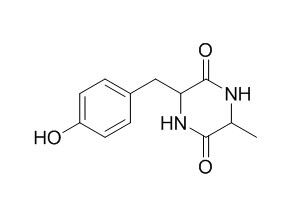
Cyclo(Ala-Tyr)
Cyclo(Val-Tyr) is a product from the culture of Pseudomonas putida.
Inquire / Order:
manager@chemfaces.com
Technical Inquiries:
service@chemfaces.com
Tel:
+86-27-84237783
Fax:
+86-27-84254680
Address:
1 Building, No. 83, CheCheng Rd., Wuhan Economic and Technological Development Zone, Wuhan, Hubei 430056, PRC
Providing storage is as stated on the product vial and the vial is kept tightly sealed, the product can be stored for up to
24 months(2-8C).
Wherever possible, you should prepare and use solutions on the same day. However, if you need to make up stock solutions in advance, we recommend that you store the solution as aliquots in tightly sealed vials at -20C. Generally, these will be useable for up to two weeks. Before use, and prior to opening the vial we recommend that you allow your product to equilibrate to room temperature for at least 1 hour.
Need more advice on solubility, usage and handling? Please email to: service@chemfaces.com
The packaging of the product may have turned upside down during transportation, resulting in the natural compounds adhering to the neck or cap of the vial. take the vial out of its packaging and gently shake to let the compounds fall to the bottom of the vial. for liquid products, centrifuge at 200-500 RPM to gather the liquid at the bottom of the vial. try to avoid loss or contamination during handling.
J Ethnopharmacol.2020, 269:113752.
Molecules.2021, 26(8):2161.
Food Research International2016, 106-113
Evid Based Complement Alternat Med.2021, 2021:5023536.
Food Chem.2016, 191:81-90
The Catharanthus Genome2022,35-83.
Molecules.2022, 27(22):7997.
ScienceAsia2024, 50,2024073:1-9
J Med Food.2020, 23(6):633-640.
Molecular & Cellular Toxicology2017, 13(3):271-278
Related and Featured Products
Wei Sheng Wu Xue Bao. 2013 Aug 4;53(8):825-31.
Anti-diatom compounds from marine bacterium Pseudomonas putida.[Pubmed:
24341274]
In order to provide more natural antifouling compounds, marine bacterium Pseudomonas putida isolated from the sponge Haliclona sp. was explored to test its anti-diatom compounds.
METHODS AND RESULTS:
The strain was identified by colonial morphology, scanning electron microscope (SEM) and 16S rDNA sequence analysis. The separation procedure was guided by bioactive (Anti-diatom) and chemical (TLC, DAD-HPLCand 1H NMR) analysis, and their structures were elucidated by spectrographic techniques. The anti-diatom activity of all purified compounds was assayed. Strain 272 isolated from the sponge Haliclona sp. was identified as Pseudomonas putida. Six diketopiperazine compounds were isolated from the culture of this strain and their structures were determined as cyclo(Leu-Pro) (1), cyclo (Leu-Ala) (2), cyclo(Phe-Ala) (3), cyclo(Val-Tyr) (4), Cyclo(Ala-Tyr) (5), cyclo(Ala-Trp) (6); Compounds 3 and 6 displayed significant anti-diatom activity with the inhibitory rate of 50% and 85% at the concentration of 50 microg/mL, respectively.
CONCLUSIONS:
The anti-diatom compounds isolated from marine bacterium Pseudomonas putida were cyclo (Phe-Ala) and cyclo (Ala-Trp).