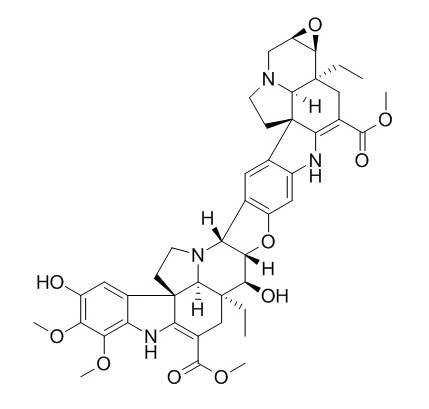
Conophylline
Conophylline is a novel differentiation inducer for pancreatic β cells, can increase the numbers of ductal cells positive for pancreatic-duodenal-homeobox protein-1 and islet-like cell clusters.
Conophylline suppresses pancreatic stellate cells and improves islet fibrosis in Goto-Kakizaki rats. It protects cells in cellular models of neurodegenerative diseases by inducing mTOR-independent autophagy.
Inquire / Order:
manager@chemfaces.com
Technical Inquiries:
service@chemfaces.com
Tel:
+86-27-84237783
Fax:
+86-27-84254680
Address:
1 Building, No. 83, CheCheng Rd., Wuhan Economic and Technological Development Zone, Wuhan, Hubei 430056, PRC
Providing storage is as stated on the product vial and the vial is kept tightly sealed, the product can be stored for up to
24 months(2-8C).
Wherever possible, you should prepare and use solutions on the same day. However, if you need to make up stock solutions in advance, we recommend that you store the solution as aliquots in tightly sealed vials at -20C. Generally, these will be useable for up to two weeks. Before use, and prior to opening the vial we recommend that you allow your product to equilibrate to room temperature for at least 1 hour.
Need more advice on solubility, usage and handling? Please email to: service@chemfaces.com
The packaging of the product may have turned upside down during transportation, resulting in the natural compounds adhering to the neck or cap of the vial. take the vial out of its packaging and gently shake to let the compounds fall to the bottom of the vial. for liquid products, centrifuge at 200-500 RPM to gather the liquid at the bottom of the vial. try to avoid loss or contamination during handling.
Bioorg Chem.2024, 152:107720.
Biocell2023, 47(8):1793-1802
Plant Methods.2017, 13:108
HortTechnology2016, 26(6):816-819
Front Pharmacol.2019, 10:1355
Evid Based Complement Alternat Med.2022, 2022:3483511
J Am Soc Mass Spectrom.2021, 32(5):1205-1214.
Anticancer Res.2024, 44(3):1033-1044.
Nat Prod Sci.2018, 24(3):206
Cells.2022, 11(8), 1311.
Related and Featured Products
J. Integr. Agr., 2013, 12(4):678-86.
Conophylline Promotes the Proliferation of Immortalized Mesenchymal Stem Cells Derived from Fetal Porcine Pancreas (iPMSCs)[Reference:
WebLink]
Conophylline, is a bis (indole) alkaloid consisting of two pentacyclic aspidosperma skeletons, isolated from Tabernaemontana divaricata, which has been found to induce b-cell differentiation in rat pancreatic acinar carcinoma cells and in cultured rat pancreatic tissue.
METHODS AND RESULTS:
We found that Conophylline can robustly stimulate iPMSCs proliferation, even promote their potential differentiation into islet-like clusters analyzed by cell counting, morphology, RT-PCR and real-time PCR, Western blotting, glucose-stimulated insulin release and insulin content analysis. The effects of Conophylline were inhibited by LY294002, which is the inhibitor of the PI3K pathway.
CONCLUSIONS:
These results suggest that Conophylline plays a key role in the regulation of cell mass proliferation, maintenance of the undifferentiated state of iPMSCs and also promotes iPMSCs differentiated into insulin-producing cells.
Int J Biochem Cell Biol. 2006;38(5-6):923-30.
Conophylline: a novel differentiation inducer for pancreatic beta cells.[Pubmed:
16337165 ]
METHODS AND RESULTS:
Among various compounds and extracts tested, we found that Conophylline, a vinca alkaloid extracted from leaves of a tropical plant Ervatamia microphylla, was effective in converting AR42J into endocrine cells. Conophylline reproduces the differentiation-inducing activity of activin A. Unlike activin A, however, Conophylline does not induce apoptosis.
To induce differentiation of AR42J cells, Conophylline increases the expression of neurogenin-3 by activating p38 mitogen-activated protein kinase. Conophylline also induces differentiation in cultured pancreatic progenitor cells obtained from fetal and neonatal rats. More importantly, Conophylline is effective in reversing hyperglycemia in neonatal streptozotocin-treated rats, and both the insulin content and the beta cell mass are increased by Conophylline. Histologically, Conophylline increases the numbers of ductal cells positive for pancreatic-duodenal-homeobox protein-1 and islet-like cell clusters.
CONCLUSIONS:
Conophylline and related compounds are useful in inducing differentiation of pancreatic beta cells both in vivo and in vitro.
Liver Int. 2014 Aug;34(7):1057-67.
Conophylline suppresses hepatic stellate cells and attenuates thioacetamide-induced liver fibrosis in rats.[Pubmed:
24119135 ]
Conophylline (CnP) is a vinca alkaloid purified from a tropical plant and inhibits activation of pancreatic stellate cells.
METHODS AND RESULTS:
We investigated the effect of CnP on hepatic stellate cells (HSC) in vitro. We also examined whether CnP attenuates hepatic fibrosis in vivo.In rat HSC and Lx-2 cells, CnP reduced the expression of α-SMA and collagen-1. CnP inhibited DNA synthesis induced by serum. CnP also promoted activation of caspase-3 and induced apoptosis as assessed by DNA ladder formation and TUNEL assay. In contrast, CnP did not induce apoptosis in AML12 cells. We then examined the effect of CnP on TAA-induced cirrhosis. In TAA-treated rats, the surface of the liver was irregular and multiple nodules were observed. Histologically, formation of pseudolobules surrounded by massive fibrous tissues was observed. When CnP was administered together with TAA, the surface of the liver was smooth and liver fibrosis was markedly inhibited. Collagen content was significantly reduced in CnP-treated liver.
CONCLUSIONS:
Conophylline suppresses HSC and induces apoptosis in vitro. CnP also attenuates formation of the liver fibrosis induced by TAA in vivo.
Diabetes. 2004 Oct;53(10):2596-602.
Promotion of beta-cell differentiation by conophylline in fetal and neonatal rat pancreas.[Pubmed:
15448089]
Conophylline is a vinca alkaloid extracted from the tropical plant Ervatamia microphylla and has been shown to induce differentiation of pancreatic AR42J cells.
METHODS AND RESULTS:
In the present study, we investigated the effect of Conophylline on the differentiation of pancreatic precursor cells. In the rat pancreatic rudiment in organ culture, Conophylline inhibited the formation of cystic structure and increased the number of insulin-positive cells. Conophylline also markedly increased the expression of mRNA for insulin and the number of pancreatic duodenal homeobox-1-positive cells. These effects of Conophylline were similar to those of activin A. We also examined the effect of Conophylline on neonatal rats treated with streptozotocin, a model of type 2 diabetes. Treatment with Conophylline significantly reduced the plasma glucose concentration and improved glucose tolerance in response to glucose loading. The insulin content and the beta-cell mass at 2 months were significantly increased by Conophylline. The number of islet-like cell clusters and pancreatic duodenal homeobox-1-positive ductal cells was greater in Conophylline-treated rats.
CONCLUSIONS:
These results suggest that Conophylline induces differentiation of pancreatic precursor cells and increases the formation of beta-cells.
Int J Oncol. 2003 Nov;23(5):1373-9.
Down-regulation of TNF-alpha receptors by conophylline in human T-cell leukemia cells.[Pubmed:
14532979]
In the course of our screening for tumor necrosis factor-alpha (TNF-alpha) function inhibitors, Conophylline, a vinca alkaloid isolated from the plant Ervatamia microphylla, was found to inhibit TNF-alpha-induced NF-kappaB activation.
METHODS AND RESULTS:
We studied the effect of Conophylline on TNF-alpha-induced NF-kappaB and JNK activations in human T-cell leukemia Jurkat cells. Conophylline inhibited both of these TNF-alpha-induced activations. It also inhibited phosphorylation and degradation of I-kappaB-alpha. Moreover, a receptor binding assay using [125I]-TNF-alpha showed that this inhibitory effect was due to a decrease in the binding of TNF-alpha to the cells. Scatchard analysis of the binding data indicated that Conophylline induced only a small change in the affinity of the receptors but a significant change in the receptor number. FACS analysis showed that Conophylline reduced the expression of CD120a/TNFR1, the high-affinity receptor for TNF-alpha, on the cell surface. On the other hand, Conophylline did not affect the kinetics of internalization and degradation of TNF-alpha/receptor complexes or the half-life of TNF-alpha binding sites.
CONCLUSIONS:
These results indicate that Conophylline down-regulates the expression of the TNF-alpha receptors on the cell surface.
J. Biol. Chem., 2015,1(10):290.
Conophylline protects cells in cellular models of neurodegenerative diseases by inducing mTOR-independent autophagy[Reference:
WebLink]
Macroautophagy is a cellular response that leads to the bulk, non-specific degradation of cytosolic components, including organelles. In recent years, it has been recognized that autophagy is essential for prevention of neurodegenerative diseases, including Parkinson disease (PD) and Huntington disease (HD).
METHODS AND RESULTS:
Here, we show that Conophylline (CNP), a vinca alkaloid, induces autophagy in an mTOR-independent manner. Using a cellular model of PD, CNP suppressed protein aggregation and protected cells from cell death caused by treatment with 1-methyl-4-phenylpyridinium (MPP+), a neuro-toxin, by inducing autophagy. Moreover, in the HD model, CNP also eliminated mutant huntingtin aggregates.
CONCLUSIONS:
Our findings demonstrate the possible use of CNP as a therapeutic drug for neurodegenerative disorders, including PD and HD.
Endocrinology. 2012 Feb;153(2):621-30.
Conophylline suppresses pancreatic stellate cells and improves islet fibrosis in Goto-Kakizaki rats.[Pubmed:
22202163 ]
METHODS AND RESULTS:
In pancreatic sections obtained from 6-wk-old GK rats, CD68-positive macrophages and glial fibrillary acidic protein- and α-smooth muscle actin-positive stellate cells infiltrated into islets. Later, the number of macrophages was increased, and the α-smooth muscle actin staining of stellate cells became stronger, indicating the involvement of stellate cells in islet fibrosis in GK rats. When Conophylline was administered orally for 4 wk, starting from 6 wk of age, invasion of stellate cells and macrophages was markedly reduced and islet fibrosis was significantly improved. The insulin content was twice as high in Conophylline-treated rats.
CONCLUSIONS:
These results indicate that Conophylline exerts antifibrotic actions both in vitro and in vivo and improves islet fibrosis in Goto-Kakizaki rats.