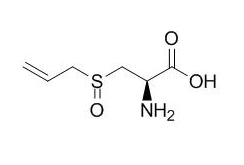
Alliin
Alliin has antiglycating potential , it offers protection against glucose or methyglyoxal induced glycation of superoxide dismutase, hence is expected to have therapeutic potential in the prevention of glycation-mediated diabetic complications. Alliin has anti-inflammatory activity, it protects against Lipopolysaccharides (LPS)-induced acute lung injury (ALI) by activating PPARγ, which subsequently inhibits LPS-induced NF-κB activation and inflammatory response; alliin has an inhibitory effect in osteoclasteogenesis with a dose-dependent manner via blocking the c-Fos-NFATc1 signaling pathway, it could be a potential therapeutic agent in the treatment of osteoporosis. Alliin and sabinene have detectable levels of antimicrobial activity.
Inquire / Order:
manager@chemfaces.com
Technical Inquiries:
service@chemfaces.com
Tel:
+86-27-84237783
Fax:
+86-27-84254680
Address:
1 Building, No. 83, CheCheng Rd., Wuhan Economic and Technological Development Zone, Wuhan, Hubei 430056, PRC
Providing storage is as stated on the product vial and the vial is kept tightly sealed, the product can be stored for up to
24 months(2-8C).
Wherever possible, you should prepare and use solutions on the same day. However, if you need to make up stock solutions in advance, we recommend that you store the solution as aliquots in tightly sealed vials at -20C. Generally, these will be useable for up to two weeks. Before use, and prior to opening the vial we recommend that you allow your product to equilibrate to room temperature for at least 1 hour.
Need more advice on solubility, usage and handling? Please email to: service@chemfaces.com
The packaging of the product may have turned upside down during transportation, resulting in the natural compounds adhering to the neck or cap of the vial. take the vial out of its packaging and gently shake to let the compounds fall to the bottom of the vial. for liquid products, centrifuge at 200-500 RPM to gather the liquid at the bottom of the vial. try to avoid loss or contamination during handling.
J Sci Food Agric.2023, 103(1):213-220.
J Cell Biochem.2024, 125(4):e30537.
Biomed Pharmacother.2021, 144:112300.
Appl. Sci.2023, 13(17):9984.
Ind Crops Prod.2014, 62:173-178
J Microbiol Biotechnol.2024, 35:e2408022.
Molecules.2020, 25(23):5556.
J Basic Clin Physiol Pharmacol.2016, 27(1):1-8
J Agric Food Chem.2017, 65(13):2670-2676
Phytomedicine.2021, 84:153501.
Related and Featured Products
Int J Mol Sci. 2016 Sep 20;17(9). pii: E1516.
Alliin Attenuated RANKL-Induced Osteoclastogenesis by Scavenging Reactive Oxygen Species through Inhibiting Nox1.[Pubmed:
27657047]
The healthy skeleton requires a perfect coordination of the formation and degradation of bone. Metabolic bone disease like osteoporosis is resulted from the imbalance of bone formation and/or bone resorption. Osteoporosis also reflects lower level of bone matrix, which is contributed by up-regulated osteoclast-mediated bone resorption. It is reported that monocytes/macrophage progenitor cells or either hematopoietic stem cells (HSCs) gave rise to multinucleated osteoclasts. Thus, inhibition of osteoclastic bone resorption generally seems to be a predominant therapy for treating osteoporosis. Recently, more and more natural compounds have been discovered, which have the ability of inhibiting osteoclast differentiation and fusion. Alliin (S-allyl-l-cysteine sulfoxides, SACSO) is the major component of aged garlic extract (AGE), bearing broad-spectrum natural antioxidant properties. However, its effects on bone health have not yet been explored.
METHODS AND RESULTS:
Hence, we designed the current study to explore its effects and role in receptor activator of nuclear factor-κB ligand (RANKL)-induced osteoclast fusion and differentiation. It was revealed that Alliin had an inhibitory effect in osteoclasteogenesis with a dose-dependent manner via blocking the c-Fos-NFATc1 signaling pathway. In addition, Alliin decreased the generation of reactive oxygen species (ROS) and down-regulated the expression of NADPH oxidase 1 (Nox1).
METHODS AND RESULTS:
The overall results revealed that Alliin could be a potential therapeutic agent in the treatment of osteoporosis.
J Ethnopharmacol. 2017 May 5;203:171-181.
Antibacterial activity of medicinal plants from The Physicians of Myddvai, a 14th century Welsh medical manuscript.[Pubmed:
28344030 ]
Antimicrobial drug resistance is a growing threat to global public health. Historical records and herbal texts relating to traditional Celtic medicine indicate an extensive pharmacopeia of plants for treating infections likely caused by microbes. However, a major barrier for successful integration of these remedies into mainstream practice is the current lack of accurate interpretation and scientific validation.
METHODS AND RESULTS:
We investigated the flora of the Isle of Arran, Scotland, via in situ targeted screening of 83 out of 138 plants identified in Meddygion Myddvai (a 14th century Welsh manuscript) to treat conditions related to microbial infections, and an additional 18 plants from modern ethnobotanical knowledge on the island (Scottish School of Herbal Medicine). In a follow-up proof-of-concept study, bioassay-guided fractionation was performed to identify bioactive constituents from two high scoring hits that inhibited Staphylococcus aureus (Gram-positive) and Escherichia coli (Gram-negative) bacterial growth.
67 historical plants (80.7%) and 14 modern plants (77.8%) were found to have detectable levels of antimicrobial activity when tested using Mobile Discovery kits, with human saliva as a source of bacteria for screening. Sabinene, a natural bicyclic monoterpene from juniper "berries" (Juniperus communis L.) and Alliin, a natural sulfoxide from garlic cloves (Allium sativum L.), were isolated and confirmed as primary antibacterial leads.
CONCLUSIONS:
Using historical medical sources such as those associated with traditional Celtic medicine to guide rigorous, evidence-based scientific investigation, provides additional leads for new and alternative bioactive molecules for combating bacterial diseases.
Microb Pathog. 2017 Jul 12;110:375-379.
Effects of alliin on LPS-induced acute lung injury by activating PPAR[Pubmed:
28711511]
Alliin is a garlic organosulfur compound that possesses various pharmacological properties.
METHODS AND RESULTS:
In the present study, the protective effects and molecular mechanism of Alliin on Lipopolysaccharides (LPS)-induced acute lung injury (ALI) were analyzed. LPS-induced ALI was induced in BALB/c mice by intranasal instillation of LPS. Alliin was administered intraperitoneally to mice 1 h after LPS treatment. The results showed that Alliin markedly inhibited lung myeloperoxidase (MPO) activity and wet/dry (W/D) ratio induced by LPS. Alliin also inhibited TNF-α and IL-1β in the bronchoalveolar lavage fluid (BALF) induced by LPS. Furthermore, LPS-induced lung pathological injury was attenuated by treatment of Alliin. LPS-induced NF-κB activation was significantly inhibited by Alliin. In addition, the expression of peroxisome proliferator-activated receptor γ (PPARγ) was up-regulated by treatment of Alliin.
CONCLUSIONS:
Taken together, these results suggested that Alliin protected against LPS-induced ALI by activating PPARγ, which subsequently inhibited LPS-induced NF-κB activation and inflammatory response. Alliin might be used as an anti-inflammatory agent in the treatment of ALI.
Int J Biol Macromol. 2017 Oct;103:182-193.
Inhibitory effect of alliin from Allium sativum on the glycation of superoxide dismutase.[Pubmed:
28502851]
Inhibition of glycation is an important approach for alleviating diabetic complications. Alliin, the most abundant sulphur compound in garlic has been demonstrated to possess antidiabetic activity. However, there is no scientific evidence supporting its antiglycating activity.
METHODS AND RESULTS:
The objective of this study was to determine the inhibitory effect of Alliin on glucose and methyglyoxal (MG)-induced glycation of an important antioxidant enzyme, superoxide dismutase (SOD). Glycation of SOD resulted in a decrease in enzyme activity, fragmentation/cross-linking, reduced cross-reactivity with anti-SOD antibodies, both tertiary and secondary structural changes, and formation of AGEs and fibrils. Alliin offered protection against glucose or MG induced glycation of SOD. The antiglycating potential of Alliin appears to be comparable with that of quercetin which is reported to be a potent natural inhibitor of glycation.
CONCLUSIONS:
Alliin has a good antiglycating effect and hence is expected to have therapeutic potential in the prevention of glycation-mediated diabetic complications.