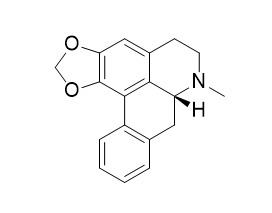
Roemerine
Roemerine is a potential active xanthine oxidase(XOD) inhibitor, XOD is a key enzyme in the pathogenesis of hyperuricemia and also a well-known target for the drug development to treat gout. Roemerine has some anti-prostate cancer effect and alleviates adverse reactions in paclitaxel combination administration. Roemerine shows significant anti-plasmodial activities with IC(50) ranged from 1.2 μM to 52.3 uM. Roemerine also possesses antibacterial activity, it improves the survival rate of septicemic BALB/c mice by increasing the cell membrane permeability of Staphylococcus aureus.
Inquire / Order:
manager@chemfaces.com
Technical Inquiries:
service@chemfaces.com
Tel:
+86-27-84237783
Fax:
+86-27-84254680
Address:
1 Building, No. 83, CheCheng Rd., Wuhan Economic and Technological Development Zone, Wuhan, Hubei 430056, PRC
Providing storage is as stated on the product vial and the vial is kept tightly sealed, the product can be stored for up to
24 months(2-8C).
Wherever possible, you should prepare and use solutions on the same day. However, if you need to make up stock solutions in advance, we recommend that you store the solution as aliquots in tightly sealed vials at -20C. Generally, these will be useable for up to two weeks. Before use, and prior to opening the vial we recommend that you allow your product to equilibrate to room temperature for at least 1 hour.
Need more advice on solubility, usage and handling? Please email to: service@chemfaces.com
The packaging of the product may have turned upside down during transportation, resulting in the natural compounds adhering to the neck or cap of the vial. take the vial out of its packaging and gently shake to let the compounds fall to the bottom of the vial. for liquid products, centrifuge at 200-500 RPM to gather the liquid at the bottom of the vial. try to avoid loss or contamination during handling.
J Sep Sci.2018, 41(11):2488-2497
Asian Pac J Cancer Prev.2021, 22(S1):97-106.
Malaysian J of Fundamental and Applied Sciences 2018, 14(3):368-373
Molecules.2021, 26(2):313.
University of Central Lancashire2017, 20472
Front Pharmacol.2021, 12:690113.
Sci Rep.2021, 11(1):11936.
JAOCS2021, 98(7):779-794.
Nutrients.2019, 12(1)
Mol Pharm.2017, 14(9):3164-3177
Related and Featured Products
Phytochemistry. 2018 May;149:123-131.
An OMIC approach to elaborate the antibacterial mechanisms of different alkaloids.[Pubmed:
29494814 ]
Plant-derived substances have regained interest in the fight against antibiotic resistance owing to their distinct antimicrobial mechanisms and multi-target properties. With the recent advances in instrumentation and analysis techniques, OMIC approaches are extensively used for target identification and elucidation of the mechanism of phytochemicals in drug discovery.
METHODS AND RESULTS:
In the current study, RNA sequencing based transcriptional profiling together with global differential protein expression analysis was used to comparatively elaborate the activities and the effects of the plant alkaloids boldine, bulbocapnine, and Roemerine along with the well-known antimicrobial alkaloid berberine in Bacillus subtilis cells. The transcriptomic findings were validated by qPCR. Images from scanning electron microscope were obtained to visualize the effects on the whole-cells.
CONCLUSIONS:
The results showed that among the three selected alkaloids, only Roemerine possessed antibacterial activity. Unlike berberine, which is susceptible to efflux through multidrug resistance pumps, Roemerine accumulated in the cells. This in turn resulted in oxidative stress and building up of reactive oxygen species, which eventually deregulated various pathways such as iron uptake. Treatment with boldine or bulbocapnine slightly affected various metabolic pathways but has not changed the growth patterns at all.
J Pharm Biomed Anal. 2017 May 30;139:37-43.
Modeling and optimizing inhibitory activities of Nelumbinis folium extract on xanthine oxidase using response surface methodology.[Pubmed:
28273649]
Xanthine oxidase (XOD), which could oxidize hypoxanthine to xanthine and then to uric acid, is a key enzyme in the pathogenesis of hyperuricemia and also a well-known target for the drug development to treat gout.
METHODS AND RESULTS:
In our study, the total alkaloids of Nelumbinis folium markedly inhibited XOD activity, with IC50 value being 3.313μg/mL. UHPLC-Q-TOF-MS and 3D docking analysis indicated that Roemerine was a potential active ingredient.
CONCLUSIONS:
A response surface methodology combined with central composite design experiment was further developed and validated for the optimization of the reaction conditions between the total alkaloids of Nelumbinis folium and XOD, which could be considered as a meaningful research for the development of XOD inhibitor rapidly and sensitively.
J Ethnopharmacol. 2013 Jan 9;145(1):381-5.
New antiplasmodial alkaloids from Stephania rotunda.[Pubmed:
23127648]
A new aporphine alkaloid named vireakine (2) along with two known alkaloids stephanine (1) and pseudopalmatine (8), described for the first time in Stephania rotunda, and together five known alkaloids tetrahydropalmatine (3), xylopinine (4), Roemerine (5), cepharanthine (6) and palmatine (7) were isolated and identified.
METHODS AND RESULTS:
The structure of the new alkaloid was established on the basis of 1D and 2D NMR experiments and mass spectrometry. The compounds were evaluated for their in vitro antiplasmodial and cytotoxic activities. All tested compounds showed significant antiplasmodial activities with IC(50) ranged from 1.2 μM to 52.3 μM with a good selectivity index for pseudopalmatine with IC(50) of 2.8 μM against W2 strain of Plasmodium falciparum and IC(50)>25 μM on K562S cells.
CONCLUSIONS:
This study provides evidence to support the use of Stephania rotunda for the treatment of malaria and/or fever by the healers. Alkaloids of the tuber exhibited antiplasmodial activity and particularly cepharanthine and pseudopalmatine.
Zhonghua Nan Ke Xue. 2017 Jan;23(1):27-33.
Anti-prostate cancer effect of roemerine: An experimental study.[Pubmed:
29658233]
To investigate the anti-prostate cancer (PCa) effect of Roemerine in vitro and in vivo in the mouse model of PCa.
METHODS AND RESULTS:
We detected the effects of Roemerine on the proliferation, apoptosis and migration of PCa cells DU145, LNCaP, PC-3 and 22RV1, screened out the sensitive cell line and constructed a tumor-bearing model in mice for verification of the antitumor efficacy of Roemerine in vivo.Roemerine inhibited the proliferation and migration of the DU145, LNCaP, PC-3 and 22RV1 cells and induced their apoptosis in different degrees, particularly those of the LNCaP cells. The average tumor weight was less in the Roemerine intervention group ([1.99±0.95] g) than in the control ([2.95±1.04] g), the least in the high-dose Roemerine (30 mg/kg) plus paclitaxel intervention group ([0.90±0.16] g). The mean heart, liver, and kidney indexes were markedly lower in the Roemerine (0.58±0.06, 6.20±0.42 and 1.49±0.33) than in the paclitaxel group (0.66±0.04, 6.99±0.72 and 1.95±0.34), while the mean spleen and thymus indexes were remarkably higher in the former (0.54±0.11 and 0.06±0.01) than in the latter (0.41±0.09 and 0.05±0.01). Pathological staining showed a lower degree of malignancy and metastasis in both the Roemerine and the Roemerine + paclitaxel intervention group than in the control, as well as a lower degree of visceral injury in the Roemerine and Roemerine + paclitaxel groups than in the paclitaxel group.
CONCLUSIONS:
Roemerine has some anti-PCa effect and alleviates adverse reactions in paclitaxel combination administration.
PLoS One. 2015 Nov 25;10(11):e0143863.
Roemerine Improves the Survival Rate of Septicemic BALB/c Mice by Increasing the Cell Membrane Permeability of Staphylococcus aureus.[Pubmed:
26606133 ]
Staphylococcus aureus is one of the most frequently occurring hospital- and community-associated pathogenic bacteria featuring high morbidity and mortality. The occurrence of methicillin-resistant S. aureus (MRSA) has increased persistently over the years. Therefore, developing novel anti-MRSA drugs to circumvent drug resistance of S. aureus is highly important.
Roemerine, an aporphine alkaloid, has previously been reported to exhibit antibacterial activity.
METHODS AND RESULTS:
The present study aimed to investigate whether Roemerine can maintain these activities against S.aureus in vivo and further explore the underlying mechanism. We found that Roemerine is effective in vitro against four S. aureus strains as well as in vivo against MRSA insepticemic BALB/c mice. Furthermore, Roemerine was found to increase cell membrane permeability in a concentration-dependent manner.
CONCLUSIONS:
These findings suggest that Roemerine may be developed as a promising compound for treating S. aureus, especially methicillin-resistant strains of these bacteria.