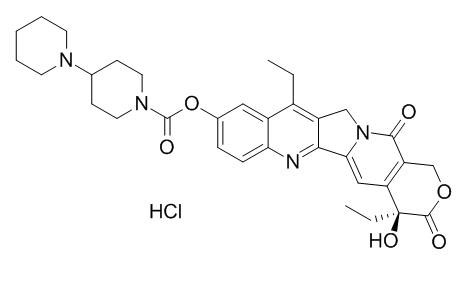
Irinotecan hydrochloride
Irinotecan hydrochloride is a water soluble topoisomerase I inhibitor mainly used to treat colon cancer and rectal cancer.
Inquire / Order:
manager@chemfaces.com
Technical Inquiries:
service@chemfaces.com
Tel:
+86-27-84237783
Fax:
+86-27-84254680
Address:
1 Building, No. 83, CheCheng Rd., Wuhan Economic and Technological Development Zone, Wuhan, Hubei 430056, PRC
Providing storage is as stated on the product vial and the vial is kept tightly sealed, the product can be stored for up to
24 months(2-8C).
Wherever possible, you should prepare and use solutions on the same day. However, if you need to make up stock solutions in advance, we recommend that you store the solution as aliquots in tightly sealed vials at -20C. Generally, these will be useable for up to two weeks. Before use, and prior to opening the vial we recommend that you allow your product to equilibrate to room temperature for at least 1 hour.
Need more advice on solubility, usage and handling? Please email to: service@chemfaces.com
The packaging of the product may have turned upside down during transportation, resulting in the natural compounds adhering to the neck or cap of the vial. take the vial out of its packaging and gently shake to let the compounds fall to the bottom of the vial. for liquid products, centrifuge at 200-500 RPM to gather the liquid at the bottom of the vial. try to avoid loss or contamination during handling.
Front Neurosci.2019, 13:1091
Curr Issues Mol Biol.2024, 46(4):3328-3341.
Int J Mol Sci.2024, 25(22):12152.
LWT2021, 138:110630.
Trop J Nat Prod Res2023, 7(12):5611-5615.
Emirates Journal of Food and Agriculture.2022, 34(6): 528-536.
Sci Rep.2021, 11(1):10931.
Asian Pac J Tropical Bio.2020, 10(6):239-247
J Neuroinflammation.2023, 20(1):268.
Biosci Rep.2020, 40(8):BSR20201219.
Related and Featured Products
Anticancer Drugs. 1994 Apr;5(2):202-6.
Activity of CPT-11 (irinotecan hydrochloride), a topoisomerase I inhibitor, against human tumor colony-forming units.[Pubmed:
8049503]
CPT-11 (Irinotecan hydrochloride, 7-ethyl-10-[4-(piperidino)-1-piperidino] carbonyloxy-camptothecin) is a semisynthetic camptothecin derivative developed in Japan.
METHODS AND RESULTS:
The inhibitory activity of CPT-11 against human tumor colony-forming units from freshly explanted human tumors was explored using a soft agar cloning system. Final CPT-11 concentrations of 0.3-3.0 micrograms/ml were used for a 1 h exposure. At a concentration of 3.0 micrograms/ml antitumor activity was seen against colorectal, ovarian, nonsmall-cell lung, breast cancer and mesothelioma colony-forming units.
CONCLUSIONS:
CPT-11 should have activity against a broad spectrum of tumors in patients.
Cancer Chemother Pharmacol. 1998;42(4):280-6.
Inhibition of intestinal microflora beta-glucuronidase modifies the distribution of the active metabolite of the antitumor agent, irinotecan hydrochloride (CPT-11) in rats.[Pubmed:
9744772]
SN-38, a metabolite of Irinotecan hydrochloride (CPT-11), is considered to play a key role in the development of diarrhea as well as in the antitumor activity of CPT-11. We have previously found that the inhibition of beta-glucuronidase, which hydrolyzes detoxified SN-38 (SN-38 glucuronide) to reform SN-38, in the lumen by eliminating the intestinal microflora with antibiotics, markedly ameliorates the intestinal toxicity of CPT-11 in rats. In this study we compared the disposition of CPT-11 and its metabolites in rats treated with and without antibiotics.
METHODS AND RESULTS:
Rats were given drinking water containing 1 mg/ml penicillin and 2 mg/ml streptomycin from 5 days before the administration of CPT-11 (60 mg/kg i.v.) and throughout the experiment. CPT-11, SN-38 glucuronide and SN-38 concentrations in the blood, intestinal tissues and intestinal luminal contents were determined by HPLC.
Antibiotics had little or no effect on the pharmacokinetics of CPT-11, SN-38 glucuronide or SN-38 in the blood, or in the tissues or contents of the small intestine, which has less beta-glucuronidase activity in its luminal contents. In contrast, antibiotics markedly reduced the AUC1-24 h of SN-38 (by about 85%) in the large intestine tissue without changing that of CPT-11, and this was accompanied by a complete inhibition of the deconjugation of SN-38 glucuronide in the luminal contents.
CONCLUSIONS:
These results suggest that SN-38, which results from the hydrolysis of SN-38 glucuronide by beta-glucuronidase in the intestinal microflora, contributes considerably to the distribution of SN-38 in the large intestine tissue, and that inhibition of the beta-glucuronidase activity by antibiotics results in decreased accumulation of SN-38 in the large intestine.