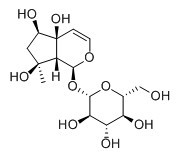
Harpagide
Harpagide has neuroprotective effect, it can obviously protect acute cerebral ischemia in mice,its therapeutical effects are approached to protecting the activity of brain mitochondria and decreasing protein expression level of caspase-3; harpagide also has a potential for prevention of bone loss in ovariectomized (OVX) mice by regulating the stimulation of osteoblast differentiation and the suppression of osteoclast formation. Harpagide may have anti-inflammatory efficacy.
Inquire / Order:
manager@chemfaces.com
Technical Inquiries:
service@chemfaces.com
Tel:
+86-27-84237783
Fax:
+86-27-84254680
Address:
1 Building, No. 83, CheCheng Rd., Wuhan Economic and Technological Development Zone, Wuhan, Hubei 430056, PRC
Providing storage is as stated on the product vial and the vial is kept tightly sealed, the product can be stored for up to
24 months(2-8C).
Wherever possible, you should prepare and use solutions on the same day. However, if you need to make up stock solutions in advance, we recommend that you store the solution as aliquots in tightly sealed vials at -20C. Generally, these will be useable for up to two weeks. Before use, and prior to opening the vial we recommend that you allow your product to equilibrate to room temperature for at least 1 hour.
Need more advice on solubility, usage and handling? Please email to: service@chemfaces.com
The packaging of the product may have turned upside down during transportation, resulting in the natural compounds adhering to the neck or cap of the vial. take the vial out of its packaging and gently shake to let the compounds fall to the bottom of the vial. for liquid products, centrifuge at 200-500 RPM to gather the liquid at the bottom of the vial. try to avoid loss or contamination during handling.
Biomimetics (Basel).2022, 7(4):154.
World J Microbiol Biotechnol.2024, 40(9):265.
Foods.2021, 10(11):2754.
Appl. Sci.2021, 11(24),12080
Journal of Functional Foods2022, 99: 105331.
Molecules.2020, 25(7):1625.
Antioxidants (Basel).2024, 13(3):340.
J Sep Sci.2019, 42(21):3352-3362
Phytother Res.2019, 33(4):1104-1113
Int J Nanomedicine.2022, 17:6513-6525.
Related and Featured Products
Bioorg Med Chem. 2011 Aug 15;19(16):4882-6.
Effects of β-glucosidase hydrolyzed products of harpagide and harpagoside on cyclooxygenase-2 (COX-2) in vitro.[Pubmed:
21775152 ]
Harpagide (1) and harpagoside (2) are two iridoid glycosides existing in many medicinal plants. Although they are believed to be the main bioactive compounds related to the anti-inflammatory efficacy of these plants, the mechanisms of their anti-inflammatory activities remain unclear.
METHODS AND RESULTS:
The results of our present study showed that 1 and 2 had no effects on inhibitions of cyclooxygenase (COX)-1/2 enzyme activity, tumor necrosis factor-α (TNF-α) release, and nitric oxide (NO) production in vitro. However, the hydrolyzed products of 1 and 2 with β-glucosidase treatment showed a significant inhibitory effect on COX-2 activity at 2.5-100 μM in a concentration-dependent manner. Our further study revealed that the hydrolyzed 2 product was structurally the same as the hydrolyzed 1 product (H-Harpagide (3)). The structure of 3 was 2-(formylmethyl)-2,3,5-trihydroxy-5-methylcyclopentane carbaldehyde, with a backbone similar to prostaglandins and COX-2 inhibitors such as celecoxib. All of them have a pentatomic ring with two adjacent side chains.
CONCLUSIONS:
The result of molecular modeling and docking study showed that 3 could bind to the COX-2 active domain well through hydrophobic and hydrogen-bonding interactions, whereas 1 and 2 could not, implying that the hydrolysis of the glycosidic bond of 1 and 2 is a pre-requisite step for their COX-2 inhibitory activity.
Journal of Chinese Pharmaceutical Sciences, 2015, 50(12):1026-31.
Neuro-protective effect of harpagide on acute cerebral ischemic injury in mice and its mechanism involving mitochondria.[Reference:
WebLink]
To observe the neuro-protective effects of Harpagide on acute cerebral ischemic injury in mice and its mechanism involving mitochondria.
METHODS AND RESULTS:
Acute cerebral ischemia were achieved by operation of MCAO in the left brain, random allocation was taken to divide ICR mice into sham group, model group, nimodipine group and Harpagide (5,10,15 mg·kg-1) groups. Mice were intraperitoneal injected Harpagide immediately after surgeiy. Nerve function score, content of brain water, brain index and the common changes of brain pathological structure in HE staining were measured: Ability of mitochondria Ca2+-Mg2+-AT-Pase and protein expression level of caspase-3 in the MCAO mice' brains was determined: Ultrastructure change of mitochondria under the TEM was observed. Compared with model group, the Harpagide groups could decreased the nerve function score, the content of brain water, brain index and the volume of ischemia in mice with different degrees in MCAO mice (P<0.05, P<0.01). 10 mg·kg-1 of Harpagide could increased the activity of Ca2+-Mg2+-ATPase obviously (P<0.01): And significantly decreased the protein expression level of caspase-3 (P<0.01): Harpagide groups could protect the pathogeny structure and the ultrastructure of mitochondria with different degrees in MCAO mice, decrease edema of mitochondria obviously.
CONCLUSIONS:
Harpagide could obviously protect acute cerebral ischemia in mice, its therapeutical effects are approached to protecting the activity of brain mitochondria and decreasing protein expression level of caspase-3.
Medical Research & Education, 2009, 26(2):11-2.
Protective effects of Harpagide and Harpagoside on human vascular endothelial cells injury induced by hydrogen peroxide.[Reference:
WebLink]
To investigate protective effects of Harpagide and Harpagoside on human vascular endothelial cells(HUVECS) injury induced by hydrogen peroxide(H2O2).
METHODS AND RESULTS:
The well grown 3-5 generations HUVECS were cultured for study and divided into control group,H2O2 group,Harpagide group and harpagoside group.The morphologic of HUVECS were observed under light microscope and HUVECS activities were determined by the methyl thiazolyl tetrazolium(MTT)assay.The contents of lactate dehydrogenises(LDH) and malonadehyde(MDA) in the supernatant of HUVECS were determined by the spectra photometric assay. Harpagide and Harpagoside made morphologic changes of HUVECS induced by H2O2 tend to normal,increased the activities of HUVECS and lessened the injury of cell membrane,decreased the contents of MDA and LDH.
CONCLUSIONS:
Harpagide and harpagoside could inhibit the injury of HUVECS induced by H2O2.
J Ethnopharmacol. 2016 Feb 17;179:66-75.
Anti-osteoporotic activity of harpagide by regulation of bone formation in osteoblast cell culture and ovariectomy-induced bone loss mouse models.[Pubmed:
26712566 ]
Harpagide, an iridoid glucoside, is a constituent of the root of Harpagophytum procumbens var. sublobatum (Engl.) Stapf, Devil's claw which has been used in patients with osteoarthritis (OA). In the present study, we investigated the anti-osteoporotic potential of Harpagide and its underlying mechanism of action in in vitro cell culture and in vivo bone loss animal models.
Harpagide was obtained from the alkalic hydrolysis of harpagoside, a major constituent of H. procumbens var. sublobatum Analysis of biomarkers for bone formation in osteoblastic MC3T3-E1 cells and bone resorption in osteoclast cells derived from mouse bone marrow cells was performed to evaluate the mechanism of action.
METHODS AND RESULTS:
The protective activity of Harpagide against bone loss was also evaluated in ovariectomized (OVX) mouse model.
Harpagide improved bone properties by stimulating the process of differentiation and maturation of osteoblast cells and suppressing the process of RANKL-induced differentiation of osteoclast cells. In OVX-induced bone loss mouse model, oral administration of Harpagide significantly improved recovery of bone mineral density, trabecular bone volume, and trabecular number in the femur. Harpagide also prevented increase of trabecular separation and structure model index induced by OVX. Harpagide effectively inhibited the serum levels of biochemical markers of bone loss, including alkaline phosphatase, osteocalcin, C-terminal telopeptide, and tartrate-resistant acid phosphatase.
CONCLUSIONS:
Taken together, the present study demonstrates that Harpagide has a potential for prevention of bone loss in OVX mice by regulating the stimulation of osteoblast differentiation and the suppression of osteoclast formation. Therefore, these findings suggest that Harpagide might serve as a bioactive compound derived from H. procumbens var. sublobatum for improvement of age-dependent bone destruction disease.