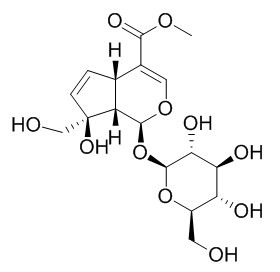
Gardenoside
Gardenoside has hepatoprotective, pain‑relieving, and anti-mastitis effects. it may be a potential therapeutic herb against NASH by suppressed supernatant inflammatory cytokine production and intracellular NFkB activity. Gardenoside may be considered potential drug candidates that target P2X3 and P2X7 purine receptors.
Inquire / Order:
manager@chemfaces.com
Technical Inquiries:
service@chemfaces.com
Tel:
+86-27-84237783
Fax:
+86-27-84254680
Address:
1 Building, No. 83, CheCheng Rd., Wuhan Economic and Technological Development Zone, Wuhan, Hubei 430056, PRC
Providing storage is as stated on the product vial and the vial is kept tightly sealed, the product can be stored for up to
24 months(2-8C).
Wherever possible, you should prepare and use solutions on the same day. However, if you need to make up stock solutions in advance, we recommend that you store the solution as aliquots in tightly sealed vials at -20C. Generally, these will be useable for up to two weeks. Before use, and prior to opening the vial we recommend that you allow your product to equilibrate to room temperature for at least 1 hour.
Need more advice on solubility, usage and handling? Please email to: service@chemfaces.com
The packaging of the product may have turned upside down during transportation, resulting in the natural compounds adhering to the neck or cap of the vial. take the vial out of its packaging and gently shake to let the compounds fall to the bottom of the vial. for liquid products, centrifuge at 200-500 RPM to gather the liquid at the bottom of the vial. try to avoid loss or contamination during handling.
Antioxidants (Basel).2024, 13(8):951.
Daru.2022, 30(2):273-288.
Biomed Pharmacother.2024, 171:116166.
Biol Pharm Bull.2020, 43(10):1534-1541.
Food Chem.2023, 427:136647.
Nutrients.2020, 12(12):3607.
Analytical methods2019, 11(6)
Antioxidants (Basel).2020, 9(6):526.
Pharmacol Res.2020, 161:105205.
Int J Mol Sci.2022, 23(21):13406.
Related and Featured Products
Int J Mol Sci . 2015 Nov 20;16(11):27749-56.
Inhibitory Effect of Gardenoside on Free Fatty Acid-Induced Steatosis in HepG2 Hepatocytes[Pubmed:
26610473]
Abstract
Gardenoside is one of the most important effective extractions of a herb for its hepatoprotective properties. The aim of this study was to address the mechanism of Gardenoside on HepG2 cellular steatosis induced by free fatty acids (FFAs). The model of HepG2 steatosis was duplicated by oleic and palmitic acid at the proportion of 2:1 (FFAs mixture) for 24 h, then lipid toxicity was induced. 3-(4,5-Dimethylthiazol-2-yl)-2,5-diphenyltetrazolium bromide (MTT) were used to detect cell viability and Oil Red O staining method was used to judge the lipid accumulation respectively. Inflammatory cytokines TNF-α, IL-1β, IL-6 and intracellular NFκB were measured after 24 h. The steatosis was significantly decreased after Gardenoside treatment without cytotoxicity. TNF-α, IL-1β, IL-6 were modulated to HepG2 cells by treatment of Gardenoside. In the meantime, the activation of NFκB was inhibited by Gardenoside. Gardenoside has a protective effect on FFA-induced cellular steatosis in HepG2 cells which indicates that Gardenoside might be a potential therapeutic herb against NASH by suppressed supernatant inflammatory cytokine production and intracellular NFkB activity.
Keywords: HepG2; NFκB; free fatty acid; Gardenoside; inflammatory cytokines; steatosis.
Chinese Journal of Information on Tcm, 2004, 11(6):500-502.
Effect of Concha Margatitifera Usta, Cholic Acid, Gardenoside, Baicalin on MCP-1 in the Ischemic Cerebral Tissue of Rats after Middle Cerebral Artery Occlusion.[Reference:
WebLink]
To study the effect of Concha Margatitifera Usta, Cholic Acid, Gardenoside, Baicalin on the protein levels of monocyte chemoattractant protein (MCP-1) in the ischemic cerebral tissue of rats after middle cerebral artery occlusion in rats.
METHODS AND RESULTS:
The 110 male SD rats were randomly assigned to the normal group, middle cerebral artery occlusion for 12 hours group and Concha Margatitifera Usta, Cholic Acid, Gardenoside, Baicalin cure middle cerebral artery occlusion for 12 hours group, middle cerebral artery occlusion for 24 hours group and Concha Margatitifera Usta, Cholic Acid, Gardenoside, Baicalin cure middle cerebral artery occlusion for 24 hours group. The protein levels of MCP-1 were measured by enzyme linked immunosorbent assay (ELISA). The protein level of MCP-1 of the ischemic cerebral tissue of rats in the middle cerebral artery occlusion for 12 hours group was markedly increased than the normal group (P0.05). The protein level of MCP-1 of the ischemic cerebral tissue of rats in Concha Margatitifera Usta and Gardenoside cure middle cerebral artery occlusion for 12 hours group were significantly lower than it in the middle cerebral artery occlusion for 12 hours group (P0.01). There was no significant change on the protein level of MCP-1 in the ischemic cerebral tissue of rats between Cholic Acid, Baicalin cure middle cerebral artery occlusion for 12 hours group and the middle cerebral artery occlusion for 12 hours group. The protein level of MCP-1 of the ischemic cerebral tissue of rats in the middle cerebral artery occlusion for 24 hours group was markedly increased than the normal group (P0.05). The protein level of MCP-1 of the ischemic cerebral tissue of rats in the Concha Margatitifera Usta, Cholic Acid, Gardenoside ,Baicalin cure middle cerebral artery occlusion for 24 hours group were significantly lower than it in the middle cerebral artery occlusion for 24 hours group (P0.05 or P0.01).
CONCLUSIONS:
Reducing the level of MCP-1 of the ischemic cerebral tissue of rats after ischemia may be one of the most important ways for the neuroprotective effects the middle cerebral artery occlusion group.
Chinese Veterinary Science, 2013, 43(8):876-880.
Inhibited effects of gardenoside on the LPS-induced mice mastitis[Reference:
WebLink]
METHODS AND RESULTS:
To investigate the protective effects of Gardenoside on the mice against mastitis,48 male and female mice were paired and randomly divided into 6 groups.Mouse mastitis models were established by pouring LPS into mammary gland after farrowing.Female mice with mastitis were treated with different concentrations of Gardenoside(25,50 and 100 mg/kg) and dexamethasone,respectively. Mammary glands of the mice were collected at 24 h after the treatment to study the effects of Gardenoside on the histopathology and the expression of myeloperoxidase(MPO),TNF-α,IL-6 and IL-1β. In result,the expression levels of TNF-α,IL-6 and IL-1β were significantly higher in the LPS group than the normal group,indicating the model of mastitis was established successfully in this study.Mammary gland pathological damages were significantly inhibited by Gardenoside treatment compared with the LPS group(P0.01).MPO expression levels were decreased with the treatment of low,medium and high doses of Gardenoside,and the expression levels of TNF-α,IL-6 and IL-1β were significantly lower in the Gardenoside group than the dexamethasone group.
CONCLUSIONS:
These results indicated that Gardenoside has inhibitory effect on mice mastitis,and the inhibitory effect exhibits a dose-dependent manner.
J Recept Signal Transduct Res . 2018 Jun;38(3):198-203.
Gardenoside suppresses the pain in rats model of chronic constriction injury by regulating the P2X3 and P2X7 receptors[Pubmed:
29932348]
Abstract
Objectives: Here, using rat model, we investigated the roles of Gardenoside in the chronic constriction injury (CCI) of the ischiadic nerve.
Methods: Bennett and Xie's unilateral sciatic nerve CCI model was used in this study. A total of 60 rats were divided into control group (CN), sham group (Sham), CCI group, and Gardenoside administrated CCI group. An aliquot of 5 mL Gardenoside solution was administrated through gavage once per day for 14 d. Mechanical withdrawal threshold (MWT) and the thermal withdrawal latency (TWL) were detected. The levels of inducible nitric oxide synthase (iNOS), interleukin-1β (IL-1β), and tumor necrosis factor-α (TNF-α) in spinal fluid were detected by ELISA. By using real-time quantitative reverse transcription polymerase chain reaction (qRT-PCR) and western blot, we analyzed the expression of P2X purinoceptor 3 and 7 (P2X3 and P2X7 receptors) in different groups. The expression of p-ERK/ERK and p-p38/p38 were also detected by western blot.
Results: We found out that Gardenoside could significantly improve the sciatica by partially restore the decrease of MWT and TWL in CCI rats. The levels of iNOS, IL-1β, and TNF-α were higher in CCI group (p < .05). The expressions of P2X3 and P2X7 were significantly increased in the CCI rats compared to control rats (p < .05). The levels of p-ERK/ERK and p-p38/p38 were also obviously increased in CCI group (p < .05). After treated with the Gardenoside, these increases were decreased.
Conclusions: These results indicated that Gardenoside may be able to relief CCI-induced neuropathic pain by regulating the P2X3 and the P2X7 expression on the ischiadic nerve.
Keywords: Gardenoside; P2X3; P2X7; inflammation; ischiadic nerve chronic constriction injury.
International Journal of Molecular Sciences, 2015, 16(11):27749-27756.
Inhibitory Effect of Gardenoside on Free Fatty Acid-Induced Steatosis in HepG2 Hepatocytes[Pubmed:
26610473]
Gardenoside is one of the most important effective extractions of a herb for its hepatoprotective properties. The aim of this study was to address the mechanism of Gardenoside on HepG2 cellular steatosis induced by free fatty acids (FFAs). The model of HepG2 steatosis was duplicated by oleic and palmitic acid at the proportion of 2:1 (FFAs mixture) for 24 h, then lipid toxicity was induced.
METHODS AND RESULTS:
3-(4,5-Dimethylthiazol-2-yl)-2,5-diphenyltetrazolium bromide (MTT) were used to detect cell viability and Oil Red O staining method was used to judge the lipid accumulation respectively. Inflammatory cytokines TNF-α, IL-1β, IL-6 and intracellular NFκB were measured after 24 h. The steatosis was significantly decreased after Gardenoside treatment without cytotoxicity. TNF-α, IL-1β, IL-6 were modulated to HepG2 cells by treatment of Gardenoside. In the meantime, the activation of NFκB was inhibited by Gardenoside.
CONCLUSIONS:
Gardenoside has a protective effect on FFA-induced cellular steatosis in HepG2 cells which indicates that Gardenoside might be a potential therapeutic herb against NASH by suppressed supernatant inflammatory cytokine production and intracellular NFkB activity.
Molecular Medicine Reports, 2018, 17(6):7980-7986.
Gardenoside combined with ozone inhibits the expression of P2X3 and P2X7 purine receptors in rats with sciatic nerve injury.[Pubmed:
29620177]
Neuropathic pain is a severe health problem for which there is a lack of effective therapy. Ozone and Gardenia fruits have been used separately in pain relief for many years; however, their underlying mechanisms remain unclear. To investigate the pain‑relieving effects of combined ozone and Gardenia, a chronic constriction sciatic nerve injury (CCI) rat model was constructed and treated with ozone and Gardenoside (Ozo&Gar), which is a compound found in Gardenia fruits.
METHODS AND RESULTS:
A total of 70 rats were randomly divided into five groups: Control (Ctrl), Ctrl + Ozo&Gar, Sham, CCI, and CCI + Ozo&Gar. The rats in the Ctrl + Ozo&Gar and CCI + Ozo&Gar groups were administered an intravenous injection of 30 μg/ml ozone and 300 μmol/l Gardenoside. The rats in the Ctrl, Sham and CCI groups were administered the same volume of saline. Pain behavior, mechanical hyperalgesia, thermal hyperalgesia, and the protein expression levels of P2X3 and P2X7 purine receptors in L4‑L5 dorsal root ganglion (DRG) were determined 15 days post‑surgery. The results demonstrated that treatment with a combination of ozone and Gardenoside increased mechanical withdrawal threshold and thermal withdrawal latency, thus confirming their pain‑relieving effects. In addition, a significant increase in the mRNA and protein expression levels of P2X3 and P2X7 was detected in the DRG of rats in the CCI group compared with in the control groups; however, following treatment with a combination of ozone and Gardenoside, the mRNA and protein expression levels of P2X3 and P2X7 receptors were significantly reduced compared with in the CCI group.
CONCLUSIONS:
These results indicated that the mechanism underlying the pain‑relieving effects of ozone and Gardenoside may be mediated by inhibition of P2X3 and P2X7 purine receptors in the DRG. This finding suggested that ozone and Gardenoside may be considered potential drug candidates that target P2X3 and P2X7 purine receptors.
J Tradit Chin Med. 2002 Mar;22(1):55-60.
Effects of different compounding of formulae on content of gardenoside in Yin Chen Hao decoction.[Pubmed:
11977525]
METHODS AND RESULTS:
In order to observe the effects of the ground and intact Zhi Zi (Fructus Gardeniae) and different combinations of the ingredients and refined single Chinese drug granules in Yin Chen Hao Decoction compound prescription on the contents of Gardenoside (an effective component of the prescription), the contents of Gardenoside were determined with reversed phase high performance liquid chromatography (HPLC), with acetonitrile-water (15:85) as mobile phase, at wave length 238 nm.
CONCLUSIONS:
The results indicated that the Gardenoside-decocted-out rates in the decoctions prepared by different combinations of the ingredients with the ground Zhi Zi (Fructus Gardeniae) all were higher significantly than those in the decoction with intact Zhi Zi (Fructus Gardeniae), and generally, different combinations of the ingredients in the decoction had only little effect on the Gardenoside-decocted-out rate.