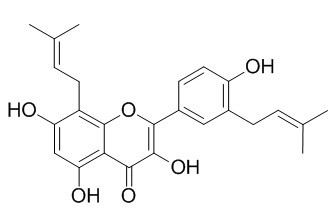
Broussoflavonol F
Broussoflavonol F has antiplatelet effect, is partially due to an inhibitory effect on cyclooxygenase, can inhibit arachidonic acid (AA)-induced platelet aggregation. Broussoflavonol F shows inhibitory activities on mushroom tyrosinase. Broussoflavonol F shows radical scavenging against 2,2-diphenyl-1-picrylhydrazyl (DPPH), the IC50 value of 708.54 uM. It also exhibits moderate cytotoxic activities against five human cancer cells with the IC50 value of 0.41-7.2 ug/mL.
Inquire / Order:
manager@chemfaces.com
Technical Inquiries:
service@chemfaces.com
Tel:
+86-27-84237783
Fax:
+86-27-84254680
Address:
1 Building, No. 83, CheCheng Rd., Wuhan Economic and Technological Development Zone, Wuhan, Hubei 430056, PRC
Providing storage is as stated on the product vial and the vial is kept tightly sealed, the product can be stored for up to
24 months(2-8C).
Wherever possible, you should prepare and use solutions on the same day. However, if you need to make up stock solutions in advance, we recommend that you store the solution as aliquots in tightly sealed vials at -20C. Generally, these will be useable for up to two weeks. Before use, and prior to opening the vial we recommend that you allow your product to equilibrate to room temperature for at least 1 hour.
Need more advice on solubility, usage and handling? Please email to: service@chemfaces.com
The packaging of the product may have turned upside down during transportation, resulting in the natural compounds adhering to the neck or cap of the vial. take the vial out of its packaging and gently shake to let the compounds fall to the bottom of the vial. for liquid products, centrifuge at 200-500 RPM to gather the liquid at the bottom of the vial. try to avoid loss or contamination during handling.
Chin. Med.J.Res. Prac.2017, 31(4)
Journal of Life Science2017, 233-240
J Korean Soc Food Sci Nutr2023, 52(12):1248-1255
Toxins (Basel).2021, 13(9):593.
Appl Biochem Biotechnol.2020, 190(2):732-744
Food Analytical Methods2020, 1-10
Adv. Anim. Vet. Sci.2024, 12(4):732-741
Applied Biological Chemistry2022, 65(85).
Appl. Sci.2020, 10(23), 8729
Heliyon.2024, 10(12):e31722.
Related and Featured Products
J Nat Prod. 1996 Sep;59(9):834-8.
Novel antiplatelet constituents from formosan moraceous plants.[Pubmed:
8864236]
Sixteen constituents from Formosan Moraceous plants were tested for their antiplatelet activities in rabbit platelet suspension and human platelet-rich plasma.
METHODS AND RESULTS:
Cycloartocarpin A, cycloheterophyllin, broussochalcone A, kazinol A, broussoaurone A, and Broussoflavonol F showed strong inhibition of arachidonic acid (AA)-induced platelet aggregation.
CONCLUSIONS:
Of the compounds tested, broussochalcone A exhibited the most potent inhibition of platelet aggregation induced by AA (IC50 = 6.8 microM). The antiplatelet effects of cycloheterophyllin, broussochalcone A, kazinol B, broussoaurone A, and Broussoflavonol F are partially due to an inhibitory effect on cyclooxygenase.
Journal of Chemical and Pharmaceutical Research, 2014, 6(6):688-69.
Antioxidant activity of flavonoid compounds from the leaves of Macaranga gigantea[Reference:
WebLink]
METHODS AND RESULTS:
Three flavonoid compounds have been isolated from the leaves of Macaranga gigantea (Euphorbiaceae) namely as glyasperin A (1), Broussoflavonol F (2), apigenin (3). Their structures were elucidated by spectroscopic methods including UV, IR, HRESIMS, 1D and 2D NMR analysis. Compounds 1–3 were evaluated for their radical scavenging against 2,2-diphenyl-1-picrylhydrazyl (DPPH), showing their IC50 were 125.10, 708.54, and 518.01 μM, respectively.
CONCLUSIONS:
The results indicate that as glyasperin A (1) more active than ascorbic acid (329.01 μM).
Food Chemistry, 2008 , 106 (2) :529-535.
Tyrosinase inhibitors from paper mulberry (Broussonetia papyrifera)[Reference:
WebLink]
METHODS AND RESULTS:
Fractionation of a chloroform-soluble extract from twigs of Broussonetia papyrifera, led to the isolation of one new compound, 3,5,7,4'-tetrahydroxy-3'-(2-hydroxy-3-methylbut-3-enyl)flavone (1), and 10 known compounds, uralenol (2), quercetin (3), isolicoflavonol (4), papyriflavonol A (5), Broussoflavonol F (6), 5,7,3',5'-tetrahydroxyflavanone (7), luteolin (8), isoliquiritigenin (9), broussochalcone A (10) and 5,7,3',4'-tetrahydroxy-3-methoxyflavone (11). Their structures were identified by interpretation of MS, 1H NMR, 13C NMR, HMQC and HMBC data.
CONCLUSIONS:
Their inhibitory activities on mushroom tyrosinase using l-tyrosine as substrate were investigated and the IC₅₀ values of 3,5,7,4'-tetrahydroxy-3'-(2-hydroxy-3-methylbut-3-enyl)flavone, uralenol, quercetin and Broussoflavonol F were found to be 96.6, 49.5, 57.8, and 82.3 μM, respectively, better than arbutin, a well-known tyrosinase inhibitor.
Nat Prod Commun. 2012 Oct;7(10):1309-10.
Dihydroflavonol and flavonol derivatives from Macaranga recurvata.[Pubmed:
23156995]
METHODS AND RESULTS:
Two new dihydroflavonol derivatives, macarecurvatins A and B, have been isolated from the leaves of Macaranga recurvata (Euphorbiaceaae), along with the known compounds diisoprenylaromadendrin, glyasperin A and Broussoflavonol F. The structures of the new compounds were determined on the basis of spectroscopic evidence.
CONCLUSIONS:
Upon cytotoxic evaluation against P-388 cells, macarecurvatin B showed strong activity with an IC50 of 0.83 microM.
Chinese Traditional & Herbal Drugs, 2010 , 12 (6) :505-515.
Chemical constituents in stem bark of Morus cathayana.[Reference:
WebLink]
To study chemical constituents in the stem bark of Morus cathayana.
METHODS AND RESULTS:
The constituents were separated and purified with chromatographic methods and their structures were elucidated by spectroscopic methods and chemical analyses. All the compounds were tested for their cytotoxicities. Results: Eleven compounds, glyasperin F (1), Broussoflavonol F (2), lespedezaflavanone C (3), isolicoflavonol (4), sanggenol B (5), sanggenol L (6), sanggenol D (7), sanggenol G (8), sanggenol A (9), dihydroquercetin (10), and quercetin (11), were isolated from the stem bark of M. cathayana.
CONCLUSIONS:
Compounds 1-3 are isolated from Morus L. for the first time. Compounds 2, 4-6, and 9 exhibit moderate cytotoxic activities against five human cancer cells with the IC50 value of 0.41-7.2 μg/mL.