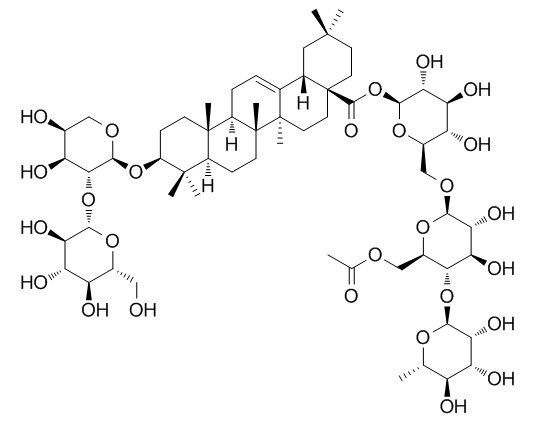
Acanthopanaxoside B
Reference standards.
Inquire / Order:
manager@chemfaces.com
Technical Inquiries:
service@chemfaces.com
Tel:
+86-27-84237783
Fax:
+86-27-84254680
Address:
1 Building, No. 83, CheCheng Rd., Wuhan Economic and Technological Development Zone, Wuhan, Hubei 430056, PRC
Providing storage is as stated on the product vial and the vial is kept tightly sealed, the product can be stored for up to
24 months(2-8C).
Wherever possible, you should prepare and use solutions on the same day. However, if you need to make up stock solutions in advance, we recommend that you store the solution as aliquots in tightly sealed vials at -20C. Generally, these will be useable for up to two weeks. Before use, and prior to opening the vial we recommend that you allow your product to equilibrate to room temperature for at least 1 hour.
Need more advice on solubility, usage and handling? Please email to: service@chemfaces.com
The packaging of the product may have turned upside down during transportation, resulting in the natural compounds adhering to the neck or cap of the vial. take the vial out of its packaging and gently shake to let the compounds fall to the bottom of the vial. for liquid products, centrifuge at 200-500 RPM to gather the liquid at the bottom of the vial. try to avoid loss or contamination during handling.
Nat Commun.2021, 12(1):681.
Food Chemistry: X2023, 101032.
Metabolites2023, 13(1), 3.
Molecules.2019, 24(21):E3834
Biomed Pharmacother.2024, 179:117365.
J Sep Sci.2021, 44(22):4064-4081.
J Biol Chem.2014, 289(3):1723-31
J Appl Biol Chem.2024, 67:33,238-244
Enzyme and Microbial Technology2022, 110002.
Microchemical Journal2024: 196:109676.
Related and Featured Products
J Nat Prod. 2006 Nov;69(11):1577-81.
Biologically active triterpenoid saponins from Acanthopanax senticosus.[Pubmed:
17125224 ]
METHODS AND RESULTS:
Three new triterpenoid saponins, acanthopanaxoside A (1), Acanthopanaxoside B (7), and acanthopanaxoside C (13), were isolated from the leaves of Acanthopanax senticosus, together with 12 known saponins. The structures of these new saponins were established as 3-O-beta-D-glucopyranosyl-(1-->2)-alpha-L-arabinopyranosyl-30-nor-olean-12,20(29)-dien-28-oic acid 28-O-alpha-L-rhamnopyranosyl-(1-->4)-6-O-acetyl-beta-D-glucopyranosyl-(1-->6)-beta-D-glucopyranosyl ester (1), 3-O-beta-D-glucopyranosyl-(1-->2)-alpha-L-arabinopyranosyl oleanolic acid 28-O-alpha-L-rhamnopyranosyl-(1-->4)-6-O-acetyl-beta-D-glucopyranosyl-(1-->6)-beta-D-glucopyranosyl ester (7), and 3-O-alpha-L-rhamnopyranosyl-(1-->2)-alpha-L-arabinopyranosyl-3beta-hydroxyolean-12-ene-28,29-dioic acid (13), on the basis of spectroscopic analysis and chemical degradation. Among the known compounds, sessiloside and tauroside H1 are reported for the first time from A. senticosus.
CONCLUSIONS:
The biological activity of compounds 1-15 was examined against pancreatic lipase. Ciwujianoside C1 (6), tauroside H1 (11), 3-O-alpha-rhamnopyranosyl-(1-->2)-alpha-arabinopyranosyl mesembryanthemoidigenic acid (12), acanthopanaxoside C (13), sessiloside (14), and chiisanoside (15) inhibited pancreatic lipase activity in vitro. In turn, ciwujianosides C2 (3), D2 (5), C4 (8), and C3 (10) and hederasaponin B (9) enhanced this enzyme.