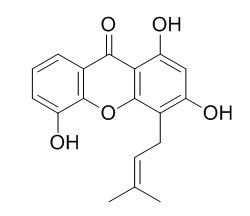
1,3,5-Trihydroxy-4-prenylxanthone
1,3,5-Trihydroxy-4-prenylxanthone is a relatively potent inhibitor of phosphodiesterase type 5 (PDE5), with an IC50 value of 3.0 μM; it shows in vitro inhibitory activity against acetylcholinesterase (AChE) and butyrylcholinesterase (BChE), with IC50 values of 56.3plusmn;0.4 and 46.0plusmn;0.3 M, respectively. 1,3,5-Trihydroxy-4-prenylxanthone inhibits LPS-induced NF-κB and AP-1 activations by interfering with the posttranslational modification (phosphorylation and/or ubiquitinylation) of IRAK-1 in the cell membrane to impede TAK1-mediated activation of IKK and MAPKs signal transduction.
Inquire / Order:
manager@chemfaces.com
Technical Inquiries:
service@chemfaces.com
Tel:
+86-27-84237783
Fax:
+86-27-84254680
Address:
1 Building, No. 83, CheCheng Rd., Wuhan Economic and Technological Development Zone, Wuhan, Hubei 430056, PRC
Providing storage is as stated on the product vial and the vial is kept tightly sealed, the product can be stored for up to
24 months(2-8C).
Wherever possible, you should prepare and use solutions on the same day. However, if you need to make up stock solutions in advance, we recommend that you store the solution as aliquots in tightly sealed vials at -20C. Generally, these will be useable for up to two weeks. Before use, and prior to opening the vial we recommend that you allow your product to equilibrate to room temperature for at least 1 hour.
Need more advice on solubility, usage and handling? Please email to: service@chemfaces.com
The packaging of the product may have turned upside down during transportation, resulting in the natural compounds adhering to the neck or cap of the vial. take the vial out of its packaging and gently shake to let the compounds fall to the bottom of the vial. for liquid products, centrifuge at 200-500 RPM to gather the liquid at the bottom of the vial. try to avoid loss or contamination during handling.
Int Immunopharmacol.2023, 123:110572.
Korean J. of Horticultural Sci. & Tech. 2017, 793-804
Planta Med.2018, 84(15):1101-1109
Trop J Nat Prod Res2023, 7(12):5611-5615.
Heliyon.2023, 9(11):e21944.
J Adv Res.2021, 35:245-257.
J Pharm Biomed Anal.2024, 251:116444.
Phytochemistry Letters2017, 449-455
Cell Rep.2022, 39(1):110643.
Biomed Pharmacother.2020, 125:109784.
Related and Featured Products
Ugaxanthone
Catalog No: CFN96469
CAS No: 13179-11-8
Price: Inquiry(manager@chemfaces.com)
Isojacareubin
Catalog No: CFN96573
CAS No: 50597-93-8
Price: Inquiry(manager@chemfaces.com)
1,3,6,8-tetrahydroxy-4-(3-methyl-2-buten-1-yl)-9H-Xanthen-9-one
Catalog No: CFN92541
CAS No: 1319198-98-5
Price: Inquiry(manager@chemfaces.com)
6-Deoxyjacareubin
Catalog No: CFN96276
CAS No: 16265-56-8
Price: Inquiry(manager@chemfaces.com)
1,3,7-Trihydroxy-2-prenylxanthone
Catalog No: CFN98022
CAS No: 20245-39-0
Price: Inquiry(manager@chemfaces.com)
1,7-Dihydroxy-3-methoxy-2-prenylxanthone
Catalog No: CFN97264
CAS No: 77741-58-3
Price: Inquiry(manager@chemfaces.com)
1,5,8-Trihydroxy-3-methoxy-2-prenylxanthone
Catalog No: CFN99202
CAS No: 110187-11-6
Price: Inquiry(manager@chemfaces.com)
1,4,5,6-Tetrahydroxy-7-prenylxanthone
Catalog No: CFN99016
CAS No: 1001424-68-5
Price: Inquiry(manager@chemfaces.com)
1,4,6-Trihydroxy-5-methoxy-7-prenylxanthone
Catalog No: CFN99675
CAS No: 160623-47-2
Price: Inquiry(manager@chemfaces.com)
O-Demethylforbexanthone
Catalog No: CFN97493
CAS No: 92609-77-3
Price: Inquiry(manager@chemfaces.com)
Nat Prod Commun. 2015 Feb;10(2):301-3.
Phosphodiesterase inhibitory activity of the flavonoids and xanthones from Anaxagorea luzonensis.[Pubmed:
25920267]
METHODS AND RESULTS:
Five flavonoids, one isoflavone and five xanthones were isolated from Anaxagorea luzonensis. Of these eleven isolated compounds, 1,3,5-Trihydroxy-4-prenylxanthone (3) was a relatively potent inhibitor of phosphodiesterase type 5 (PDE5), with an IC50 value of 3.0 μM.
CONCLUSIONS:
This is the first report showing that natural xanthones can exhibit promising PDE5 inhibitory activity. Moreover, this study revealed that the presence of the C-4 prenyl residue attached to the xanthone core is correlated with the significant PDE5 inhibitory activity.
Journal of Medicinal Plant Research, 2012 , 6 (21):3781-3785.
Cholinesterase inhibitory activities of xanthones from Anaxagorea luzonensis A. Gray[Reference:
WebLink]
METHODS AND RESULTS:
Five xanthones (1-5) were isolated from the heartwood of Anaxagorea luzonensis A. Gray (Annonaceae) and this is the first report of the isolation of xanthone 1 (6-deoxyisojacareubin) from this species. The in vitro inhibitory activity against acetylcholinesterase (AChE) and butyrylcholinesterase (BChE) of these isolated xanthones was highest in 1,3,5-Trihydroxy-4-prenylxanthone (3) for both enzymes with IC50 values of 56.3±0.4 and 46.0±0.3 μM, respectively.
CONCLUSIONS:
The presence of the C-4 prenyl residue attached to the xanthone core co-orrelated significantly with the AChE and BChE inhibitory activities and was significantly reduced by hydroxylation (removal of the carbon double bond and addition of a hydroxyl group).
Biochem Pharmacol. 2011 Mar 15;81(6):752-60.
1,3,5-trihydroxy-4-prenylxanthone represses lipopolysaccharide-induced iNOS expression via impeding posttranslational modification of IRAK-1.[Pubmed:
21232528]
1,3,5-Trihydroxy-4-prenylxanthone (TH-4-PX) isolated from Cudrania cochinchinensis repressed lipopolysaccharide (LPS)-induced NO production in RAW264.7 macrophages.
METHODS AND RESULTS:
Here we further examined the underlying mechanisms using RT-PCR and Western blot analyses. Consistent with NO inhibition, suppression of LPS-induced iNOS expression by 1,3,5-Trihydroxy-4-prenylxanthone through abolishing IκB kinase (IKK) phosphorylation, IκB degradation and nuclear factor-κB (NF-κB) nuclear translocation was observed. After LPS stimulation, the increased nuclear level of c-Fos and c-Jun (major components of activator protein-1, AP-1) and the phosphorylated level of upstream signal molecules, such as c-Jun NH2-terminal kinase (JNK) and extracellular signal-regulated kinase, (ERK) were all significantly suppressed by 1,3,5-Trihydroxy-4-prenylxanthone, while p38 remained unaffected. A further experiment revealed that 1,3,5-Trihydroxy-4-prenylxanthone inhibited the phosphorylation of transforming growth factor-β (TGF-β)-activated kinase 1 (TAK1), an upstream signaling molecule required for IKK and mitogen-activated protein kinases (MAPKs) activation. Interestingly, the modified pattern of IRAK-1 in the presence LPS was significantly attenuated by 1,3,5-Trihydroxy-4-prenylxanthone treatment.
CONCLUSIONS:
In conclusion, 1,3,5-Trihydroxy-4-prenylxanthone inhibited LPS-induced NF-κB and AP-1 activations by interfering with the posttranslational modification (phosphorylation and/or ubiquitinylation) of IRAK-1 in the cell membrane to impede TAK1-mediated activation of IKK and MAPKs signal transduction.